Real-Time Spatiotemporal Control of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Thermal Ablation Using Echo Decorrelation Imaging in ex Vivo Bovine Liver
- PMID: 29074273
- PMCID: PMC5712268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.09.007
Real-Time Spatiotemporal Control of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Thermal Ablation Using Echo Decorrelation Imaging in ex Vivo Bovine Liver
Abstract
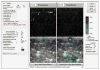
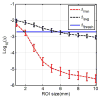
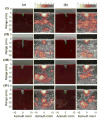
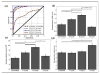
The ability to control high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) thermal ablation using echo decorrelation imaging feedback was evaluated in ex vivo bovine liver. Sonications were automatically ceased when the minimum cumulative echo decorrelation within the region of interest exceeded an ablation control threshold, determined from preliminary experiments as -2.7 (log-scaled decorrelation per millisecond), corresponding to 90% specificity for local ablation prediction. Controlled HIFU thermal ablation experiments were compared with uncontrolled experiments employing two, five or nine sonication cycles. Means and standard errors of the lesion width, area and depth, as well as receiver operating characteristic curves testing ablation prediction performance, were computed for each group. Controlled trials exhibited significantly smaller average lesion area, width and treatment time than five-cycle or nine-cycle uncontrolled trials and also had significantly greater prediction capability than two-cycle uncontrolled trials. These results suggest echo decorrelation imaging is an effective approach to real-time HIFU ablation control.
Keywords: Echo decorrelation imaging; High-intensity focused ultrasound; Real-time control; Thermal ablation.
Copyright © 2018 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Bataineh O, Jenne J, Huber P. Clinical and future applications of high intensity focused ultrasound in cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012;38:346–353. - PubMed
-
- Aubry JF, Pauly KB, Moonen C, Haar G, Ries M, Salomir R, Sokka S, Sekins KM, Shapira Y, Ye F, Huff-Simonin H, Eames M, Hananel A, Kassell N, Napoli A, Hwang JH, Wu F, Zhang L, Melzer A, Kim YS, Gedroyc WM. The road to clinical use of high-intensity focused ultrasound for liver cancer: Technical and clinical consensus. J Ther Ultrasound. 2013;1:13. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barthe PG, Slayton MH, Jaeger PM, Makin IRS, Gallagher LA, Mast TD, Runk MM, Faidi W. Ultrasound therapy system and ablation results utilizing miniature imaging/therapy arrays. IEEE Int Ultrason Symp. 2004;3:1792–1795.
-
- Bohris C, Schreiber WG, Jenne J, Simiantonakis I, Rastert R, Zabel H, Huber P, Bader R, Brix G. Quantitative MR temperature monitoring of high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;17:603–610. - PubMed
-
- Bour P, Marquet F, Ozenne V, Toupin S, Dumont E, Aubry JF, Lepetit-Coiffe M, Quesson B. Real-time monitoring of tissue displacement and temperature changes during MR-guided high intensity focused ultrasound. Magn Reson Med. 2017 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

