Intermittent but not sustained moderate hypoxia elicits long-term facilitation of hypoglossal motor output
- PMID: 29074449
- PMCID: PMC6768075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2017.10.005
Intermittent but not sustained moderate hypoxia elicits long-term facilitation of hypoglossal motor output
Abstract
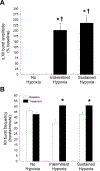
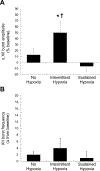
Phrenic long-term facilitation (pLTF) is a form of serotonin-dependent respiratory motor plasticity induced by moderate acute intermittent hypoxia (AIH), but not by moderate acute sustained hypoxia (ASH) of similar cumulative duration. Thus, moderate AIH-induced pLTF is sensitive to the pattern of hypoxia. On the other hand, pLTF induced by severe AIH protocols is neither pattern sensitive nor serotonin dependent (it converts to an adenosine-dependent mechanism). Although moderate AIH also induces hypoglossal LTF (hLTF), no data are available concerning its sensitivity/insensitivity to the pattern of hypoxia. Since hLTF following moderate hypoxia is serotonin-dependent, we hypothesized that hLTF is pattern-sensitive, similar to serotonin-dependent pLTF. Integrated hypoglossal nerve activity was recorded in urethane-anesthetized, vagotomized, paralyzed, and ventilated rats exposed to isocapnic AIH (3, 5min episodes of 11% O2) or ASH (a single 25min episode of 11% O2). Similar to previous studies of pLTF, hypoglossal motor output was elevated for more than 1h following AIH (50±20%, p<0.01), but not ASH (-6±9%, p>0.05). Frequency LTF was not observed following either hypoxic exposure. Thus, in agreement with our hypothesis, hypoglossal LTF following moderate AIH is pattern-sensitive, similar to phrenic LTF.
Keywords: Control of breathing; Hypoxia; Pattern; Plasticity.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Appleton‐Knapp SL, Bjork RA, Wickens TD, 2005. Examining the Spacing Effect in Advertising: Encoding Variability, Retrieval Processes, and Their Interaction. The Journal of Consumer Research 32, 266–276.
-
- Bach KB, Mitchell GS, 1996. Hypoxia-induced long-term facilitation of respiratory activity is serotonin dependent. Respir Physiol 104, 251–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

