EBV latent membrane protein 2A orchestrates p27kip1 degradation via Cks1 to accelerate MYC-driven lymphoma in mice
- PMID: 29074502
- PMCID: PMC5721284
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-07-796821
EBV latent membrane protein 2A orchestrates p27kip1 degradation via Cks1 to accelerate MYC-driven lymphoma in mice
Abstract
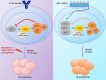
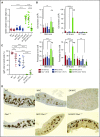
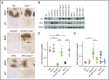
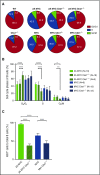
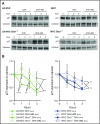
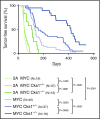
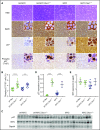
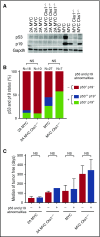
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) establishes lifelong infection in B lymphocytes of most human hosts and is associated with several B lymphomas. During latent infection, EBV encodes latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) to promote the survival of B cells by mimicking host B-cell receptor signaling. By studying the roles of LMP2A during lymphoma development in vivo, we found that LMP2A mediates rapid MYC-driven lymphoma onset by allowing B cells to bypass MYC-induced apoptosis mediated by the p53 pathway in our transgenic mouse model. However, the mechanisms used by LMP2A to facilitate transformation remain elusive. In this study, we demonstrate a key role of LMP2A in promoting hyperproliferation of B cells by enhancing MYC expression and MYC-dependent degradation of the p27kip1 tumor suppressor. Loss of the adaptor protein cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit 1 (Cks1), a cofactor of the SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase complex and a downstream target of MYC, increases p27kip1 expression during a premalignant stage. In mice that express LMP2A, Cks1 deficiency reduces spleen weights, restores B-cell follicle formation, impedes cell cycle progression of pretumor B cells, and eventually prolongs MYC-driven tumor onset. This study demonstrates that LMP2A uses the role of MYC in the cell cycle, particularly in the p27kip1 degradation process, to accelerate lymphomagenesis in vivo. Thus, our results reveal a novel mechanism of EBV in diverting the functions of MYC in malignant transformation and provide a rationale for targeting EBV's roles in cell cycle modulation.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Longnecker R, Kieff E, Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr Virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, eds. Fields Virology. 6th ed Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013:1898-1959
-
- Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet. 1964;283(7335):702-703. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell RG, Wilson JB, Anderson SJ, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A drives B cell development and survival in the absence of normal B cell receptor signals. Immunity. 1998;9(3):405-411. - PubMed
-
- Casola S, Otipoby KL, Alimzhanov M, et al. . B cell receptor signal strength determines B cell fate. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(3):317-327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

