A bone-resorption surface-targeting nanoparticle to deliver anti-miR214 for osteoporosis therapy
- PMID: 29075114
- PMCID: PMC5648312
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S139775
A bone-resorption surface-targeting nanoparticle to deliver anti-miR214 for osteoporosis therapy
Abstract
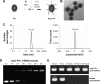
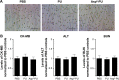
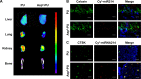
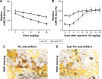
With increasing fracture risks due to fragility, osteoporosis is a global health problem threatening postmenopausal women. In these patients, osteoclasts play leading roles in bone loss and fracture. How to inhibit osteoclast activity is the key issue for osteoporosis treatment. In recent years, miRNA-based gene therapy through gene regulation has been considered a potential therapeutic method. However, in light of the side effects, the use of therapeutic miRNAs in osteoporosis treatment is still limited by the lack of tissue/cell-specific delivery systems. Here, we developed polyurethane (PU) nanomicelles modified by the acidic peptide Asp8. Our data showed that without overt toxicity or eliciting an immune response, this delivery system encapsulated and selectively deliver miRNAs to OSCAR+ osteoclasts at bone-resorption surface in vivo. With the Asp8-PU delivery system, anti-miR214 was delivered to osteoclasts, and bone microarchitecture and bone mass were improved in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice. Therefore, Asp8-PU could be a useful bone-resorption surface-targeting delivery system for treatment of osteoclast-induced bone diseases and aging-related osteoporosis.
Keywords: bone resorption; microRNA; nanoparticle; osteoporosis; targeting delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-155 inhibition up-regulates LEPR to inhibit osteoclast activation and bone resorption via activation of AMPK in alendronate-treated osteoporotic mice.IUBMB Life. 2019 Dec;71(12):1916-1928. doi: 10.1002/iub.2131. Epub 2019 Jul 18. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 31317664
-
Osteoblast-Targeting-Peptide Modified Nanoparticle for siRNA/microRNA Delivery.ACS Nano. 2016 Jun 28;10(6):5759-68. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b07828. Epub 2016 May 18. ACS Nano. 2016. PMID: 27176123
-
A delivery system specifically approaching bone resorption surfaces to facilitate therapeutic modulation of microRNAs in osteoclasts.Biomaterials. 2015 Jun;52:148-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25818421
-
Current and emerging bone resorption inhibitors for the treatment of osteoporosis.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2025 Feb;26(3):265-278. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2025.2451741. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 39797385 Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in osteoclasts and osteoporosis.RNA Biol. 2014;11(11):1355-63. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2014.996462. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 25692234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curative Cell and Gene Therapy for Osteogenesis Imperfecta.J Bone Miner Res. 2022 May;37(5):826-836. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4549. Epub 2022 Apr 17. J Bone Miner Res. 2022. PMID: 35306687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-291a-3p regulates the BMSCs differentiation via targeting DKK1 in dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Jan;36(1):35-42. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12134. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31729834 Free PMC article.
-
Non-viral based miR delivery and recent developments.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018 Jul;128:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.04.018. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018. PMID: 29679644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Supplement by Tetracycline guided amorphous Calcium Carbonate potentiates Osteoblast promotion for Synergetic Osteoporosis Therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(19):8591-8605. doi: 10.7150/thno.45142. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32754265 Free PMC article.
-
Delineation of the 1q24.3 microdeletion syndrome provides further evidence for the potential role of non-coding RNAs in regulating the skeletal phenotype.Bone. 2021 Jan;142:115705. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115705. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Bone. 2021. PMID: 33141070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lippuner K. Osteoporosis: a global challenge? Ther Umsch. 2012;69(3):135–136. German. - PubMed
-
- Melton LJ, 3rd, Johnell O, Lau E, Mautalen CA, Seeman E. Osteoporosis and the global competition for health care resources. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(7):1055–1058. - PubMed
-
- Høiberg MP, Rubin KH, Hermann AP, Brixen K, Abrahamsen B. Diagnostic devices for osteoporosis in the general population: a systematic review. Bone. 2016;92:58–69. - PubMed
-
- Sipos W, Pietschmann P, Rauner M. Strategies for novel therapeutic approaches targeting cytokines and signaling pathways of osteoclasto- and osteoblastogenesis in the fight against immune-mediated bone and joint diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(2):127–136. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

