Diversity and evolution of drug resistance mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 29075131
- PMCID: PMC5648319
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S144446
Diversity and evolution of drug resistance mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Diversity and evolution of drug resistance mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis [Corrigendum].Infect Drug Resist. 2017 Dec 20;11:1. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S159209. eCollection 2018. Infect Drug Resist. 2017. PMID: 29319057 Free PMC article.
Abstract
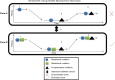
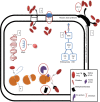
Despite the efficacy of antibiotics to protect humankind against many deadly pathogens, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, nothing can prevent the emergence of drug-resistant strains. Several mechanisms facilitate drug resistance in M. tuberculosis including compensatory evolution, epistasis, clonal interference, cell wall integrity, efflux pumps, and target mimicry. In this study, we present recent findings relevant to these mechanisms, which can enable the discovery of new drug targets and subsequent development of novel drugs for treatment of drug-resistant M. tuberculosis.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; antibiotic resistance; compensatory evolution; efflux pumps; epistasis; fitness cost.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report 2016. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. [Accessed October 4, 2017]. Available from: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

