Comparative characterization of all cellulosomal cellulases from Clostridium thermocellum reveals high diversity in endoglucanase product formation essential for complex activity
- PMID: 29075324
- PMCID: PMC5651568
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-017-0928-4
Comparative characterization of all cellulosomal cellulases from Clostridium thermocellum reveals high diversity in endoglucanase product formation essential for complex activity
Abstract
Background: Clostridium thermocellum is a paradigm for efficient cellulose degradation and a promising organism for the production of second generation biofuels. It owes its high degradation rate on cellulosic substrates to the presence of supra-molecular cellulase complexes, cellulosomes, which comprise over 70 different single enzymes assembled on protein-backbone molecules of the scaffold protein CipA.
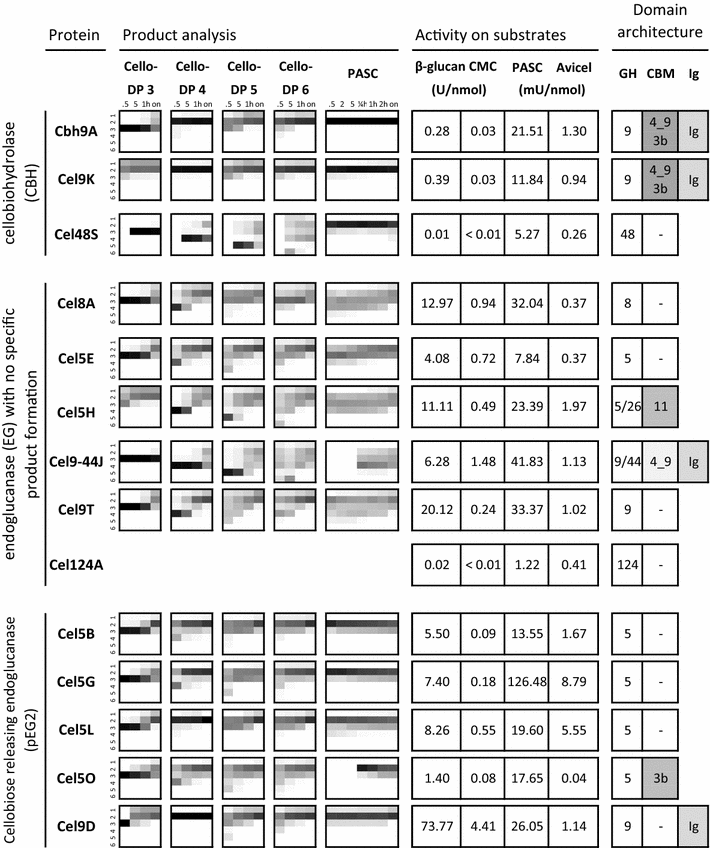
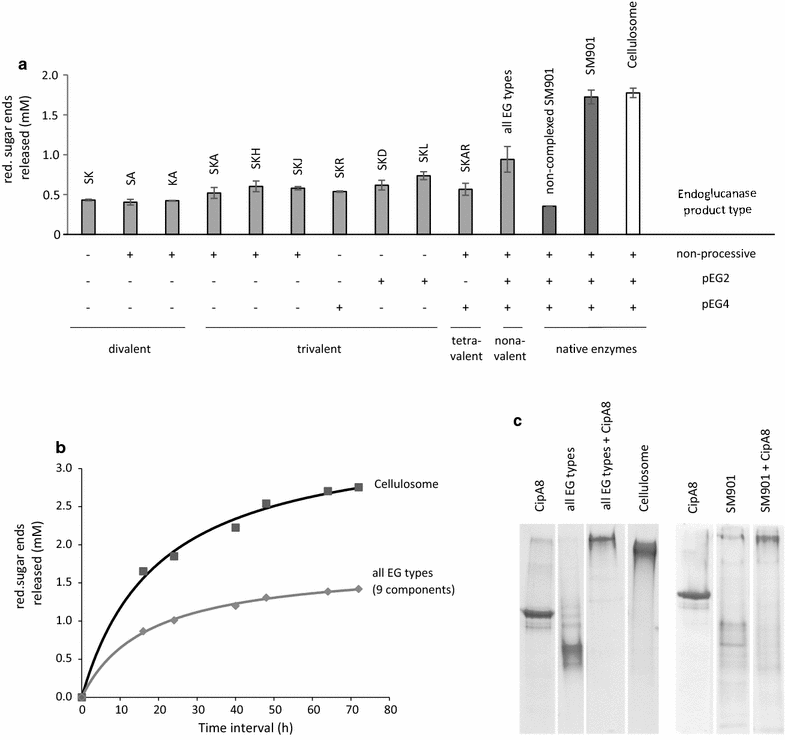
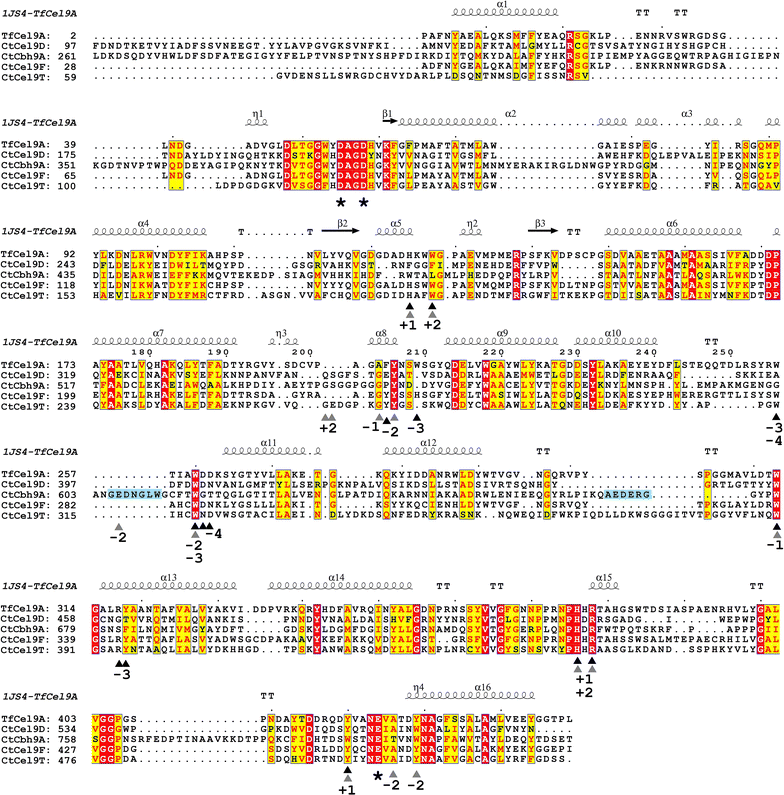
Results: Although all 24 single-cellulosomal cellulases were described previously, we present the first comparative catalogue of all these enzymes together with a comprehensive analysis under identical experimental conditions, including enzyme activity, binding characteristics, substrate specificity, and product analysis. In the course of our study, we encountered four types of distinct enzymatic hydrolysis modes denoted by substrate specificity and hydrolysis product formation: (i) exo-mode cellobiohydrolases (CBH), (ii) endo-mode cellulases with no specific hydrolysis pattern, endoglucanases (EG), (iii) processive endoglucanases with cellotetraose as intermediate product (pEG4), and (iv) processive endoglucanases with cellobiose as the main product (pEG2). These modes are shown on amorphous cellulose and on model cello-oligosaccharides (with degree of polymerization DP 3 to 6). Artificial mini-cellulosomes carrying combinations of cellulases showed their highest activity when all four endoglucanase-groups were incorporated into a single complex. Such a modeled nonavalent complex (n = 9 enzymes bound to the recombinant scaffolding protein CipA) reached half of the activity of the native cellulosome. Comparative analysis of the protein architecture and structure revealed characteristics that play a role in product formation and enzyme processivity.
Conclusions: The identification of a new endoglucanase type expands the list of known cellulase functions present in the cellulosome. Our study shows that the variety of processivities in the enzyme complex is a key enabler of its high cellulolytic efficiency. The observed synergistic effect may pave the way for a better understanding of the enzymatic interactions and the design of more active lignocellulose-degrading cellulase cocktails in the future.
Keywords: Biomass degradation; Cellobiohydrolase; Cellulase; Cellulosome; Endoglucanase; Molecular docking; Synergistic hydrolysis; Synthetic complex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modular Organization of the Thermobifida fusca Exoglucanase Cel6B Impacts Cellulose Hydrolysis and Designer Cellulosome Efficiency.Biotechnol J. 2017 Oct;12(10). doi: 10.1002/biot.201700205. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 28901714
-
Interplay between Clostridium thermocellum family 48 and family 9 cellulases in cellulosomal versus noncellulosomal states.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 May;76(10):3236-43. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00009-10. Epub 2010 Mar 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20348303 Free PMC article.
-
A major new component in the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum is a processive endo-beta-1,4-glucanase producing cellotetraose.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005 Aug 15;249(2):353-8. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.06.037. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005. PMID: 16006068
-
Processivity and the Mechanisms of Processive Endoglucanases.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;190(2):448-463. doi: 10.1007/s12010-019-03096-w. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31378843 Review.
-
The Clostridium cellulovorans cellulosome: an enzyme complex with plant cell wall degrading activity.Chem Rec. 2001;1(1):24-32. doi: 10.1002/1528-0691(2001)1:1<24::AID-TCR5>3.0.CO;2-W. Chem Rec. 2001. PMID: 11893054 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of promoter sequences for the secretory production of a Clostridium thermocellum cellulase in Paenibacillus polymyxa.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Dec;102(23):10147-10159. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9369-7. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30259100
-
Composition and yield of non-cellulosic and cellulosic sugars in soluble and particulate fractions during consolidated bioprocessing of poplar biomass by Clostridium thermocellum.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2022 Feb 28;15(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13068-022-02119-9. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2022. PMID: 35227303 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of consolidated bio-saccharification biocatalyst and process optimization for highly efficient lignocellulose solubilization.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Feb 18;12:35. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1374-2. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 30820245 Free PMC article.
-
Handling gene and protein names in the age of bioinformatics: the special challenge of secreted multimodular bacterial enzymes such as the cbhA/cbh9A gene of Clostridium thermocellum.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Feb 26;34(3):42. doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2424-9. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29480332 Review.
-
Editorial: Microorganisms for Consolidated 2nd Generation Biorefining.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 17;13:940610. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.940610. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35783433 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Koshland DE. Stereochemistry and the mechanism of enzymatic reactions. Biol Rev. 1953;28(4):416–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.1953.tb01386.x. - DOI
-
- Horn SJ, Sorlie M, Vårum KM, Väljamäe P, Eijsink VGH. Chapter five—measuring processivity. In: Harry JG, editor. Methods in Enzymology. London: Academic Press; 2012. pp. 69–95. - PubMed
-
- Wilson DB, Kostylev M. Cellulase processivity. In: Himmel EM, editor. Biomass conversion: methods and protocols. Totowa: Humana Press; 2012. pp. 93–99.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

