Sustainable carbon sources for microbial organic acid production with filamentous fungi
- PMID: 29075326
- PMCID: PMC5651581
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-017-0930-x
Sustainable carbon sources for microbial organic acid production with filamentous fungi
Abstract
Background: The organic acid producer Aspergillus oryzae and Rhizopus delemar are able to convert several alternative carbon sources to malic and fumaric acid. Thus, carbohydrate hydrolysates from lignocellulose separation are likely suitable as substrate for organic acid production with these fungi.
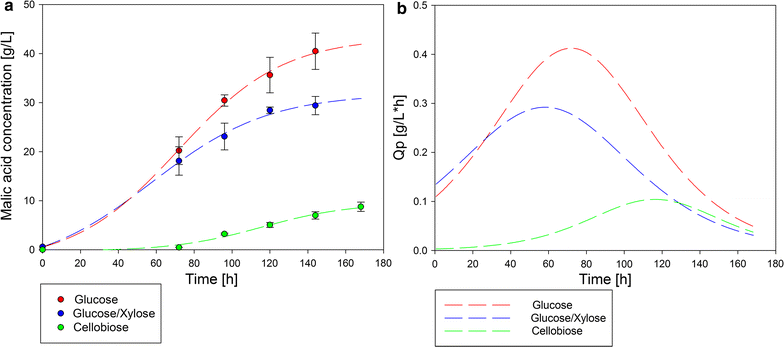
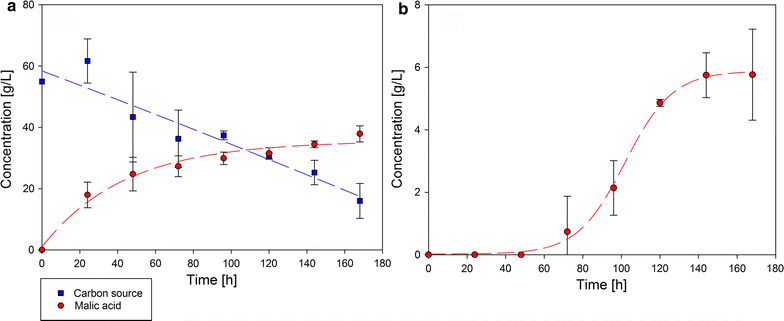
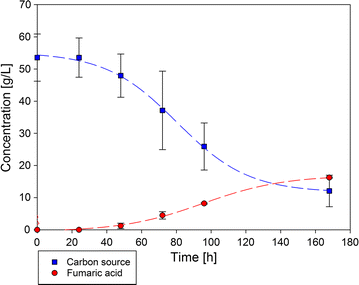
Results: Before lignocellulose hydrolysate fractions were tested as substrates, experiments with several mono- and disaccharides, possibly present in pretreated biomass, were conducted for their suitability for malic acid production with A. oryzae. This includes levoglucosan, glucose, galactose, mannose, arabinose, xylose, ribose, and cellobiose as well as cheap and easy available sugars, e.g., fructose and maltose. A. oryzae is able to convert every sugar investigated to malate, albeit with different yields. Based on the promising results from the pure sugar conversion experiments, fractions of the organosolv process from beechwood (Fagus sylvatica) and Miscanthus giganteus were further analyzed as carbon source for cultivation and fermentation with A. oryzae for malic acid and R. delemar for fumaric acid production. The highest malic acid concentration of 37.9 ± 2.6 g/L could be reached using beechwood cellulose fraction as carbon source in bioreactor fermentation with A. oryzae and 16.2 ± 0.2 g/L fumaric acid with R. delemar.
Conclusions: We showed in this study that the range of convertible sugars for A. oryzae is even higher than known before. We approved the suitability of fiber/cellulose hydrolysate obtained from the organosolv process as carbon source for A. oryzae in shake flasks as well as in a small-scale bioreactor. The more challenging hemicellulose fraction of F. sylvatica was also positively evaluated for malic acid production with A. oryzae.
Keywords: Aspergillus oryzae; Fermentation; Filamentous fungi; Levoglucosan; Lignocellulose; Malate; Malic acid; Organic acid; Organosolv; Rhizopus delemar.
Figures


References
-
- Werpy T, Petersen G. Top value added chemicals from biomass. Volume I-Results of screening for potential candidates from sugars and synthesis gas top value added chemicals from biomass Volume I : Results of Screening for Potential Candidates. US Department Energy, Washington. 2004.
-
- Miltenberger K. Hydroxycarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic. Ullmann’s Encycl Ind Chem. 2000;18:394–427.
-
- Lohbeck K, Haferkorn H, Fuhrmann W, Fedtke NC. In: Elvers B, editor. Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA; 2000. p. 145–55. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_053.
-
- Peleg Y, Stieglitz B, Goldberg I. Malic acid accumulation by Aspergillus flavus. I. Biochemical aspects of acid biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1988;28:69–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00250501. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

