The Role of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Insulin Signaling
- PMID: 29077002
- PMCID: PMC5707648
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9111176
The Role of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Insulin Signaling
Abstract
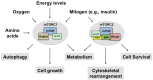
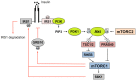
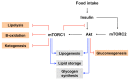
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a serine/threonine kinase that controls a wide spectrum of cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism. mTOR forms two distinct multiprotein complexes known as mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2), which are characterized by the presence of raptor and rictor, respectively. mTOR controls insulin signaling by regulating several downstream components such as growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 (Grb10), insulin receptor substrate (IRS-1), F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 8 (Fbw8), and insulin like growth factor 1 receptor/insulin receptor (IGF-IR/IR). In addition, mTORC1 and mTORC2 regulate each other through a feedback loop to control cell growth. This review outlines the current understanding of mTOR regulation in insulin signaling in the context of whole body metabolism.
Keywords: insulin; mTOR complex1 (mTORC1); mTOR complex2 (mTORC2); mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR); protein kinase B (PKB/Akt).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
mTORC1 and mTORC2 regulate insulin secretion through Akt in INS-1 cells.J Endocrinol. 2013 Jan 2;216(1):21-9. doi: 10.1530/JOE-12-0351. Print 2013 Jan. J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23092880
-
mTORC2 promotes type I insulin-like growth factor receptor and insulin receptor activation through the tyrosine kinase activity of mTOR.Cell Res. 2016 Jan;26(1):46-65. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.133. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 26584640 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Increases IGFBP-1 Phosphorylation Mediated by mTOR Inhibition.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Feb;30(2):201-16. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1194. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26714229 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 by mTORC2 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2).Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Aug;41(4):896-901. doi: 10.1042/BST20130018. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 23863152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse signaling mechanisms of mTOR complexes: mTORC1 and mTORC2 in forming a formidable relationship.Adv Biol Regul. 2019 May;72:51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Adv Biol Regul. 2019. PMID: 31010692 Review.
Cited by
-
mTOR Inhibitor Therapy and Metabolic Consequences: Where Do We Stand?Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Jun 24;2018:2640342. doi: 10.1155/2018/2640342. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30034573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Brief Narrative Review of the Underlying Mechanisms Whereby Omega-3 Fatty Acids May Influence Skeletal Muscle: From Cell Culture to Human Interventions.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 28;15(13):2926. doi: 10.3390/nu15132926. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IUGR with catch-up growth programs impaired insulin sensitivity through LRP6/IRS-1 in male rats.Endocr Connect. 2022 Jan 10;11(1):e210203. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0203. Endocr Connect. 2022. PMID: 34825892 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy: A Potential Therapeutic Target of Polyphenols in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 29;12(3):562. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030562. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32121322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anti-diabetic effects of NAG-1/GDF15 on HFD/STZ-induced mice.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 22;11(1):15027. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94581-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34294853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarbassov D.D., Ali S.M., Kim D.H., Guertin D.A., Latek R.R., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Sabatini D.M. Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:1296–1302. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.06.054. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

