Binding of Harmine Derivatives to DNA: A Spectroscopic Investigation
- PMID: 29077046
- PMCID: PMC6150274
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22111831
Binding of Harmine Derivatives to DNA: A Spectroscopic Investigation
Abstract
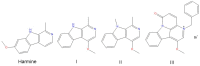
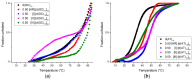
Harmine belongs to a group of β-carboline alkaloids endowed with antitumor properties. Harmine and its derivatives are thought to bind to DNA and interfere with topoisomerase activities. We investigated the base-dependent binding of harmine, and three of its synthetic anticancer-active derivatives to the genomic DNA from calf thymus and two synthetic 20-mer double helices, the poly(dG-dC)·poly(dG-dC) and the poly(dA-dT)·poly(dA-dT), by means of UV-Vis and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopies. The data show that the DNA binding and stabilising properties of the investigated derivatives are base pair-dependent. These results could be used as a guide to design and develop further bioactive analogues.
Keywords: DNA duplex; alkaloids; spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Siddiqui S., Khan O.Y., Faizi S., Siddiqui B.S. Studies on the chemical-constituents of the seeds of Peganum harmala. Isolation and structure of a new β-carboline alkaloid. Harmalicine. Heterocycles. 1987;26:1563–1567. doi: 10.3987/R-1987-06-1563. - DOI
-
- Siddiqui S., Khan O.Y., Faizi S., Siddiqui B.S. Studies on the chemical-constituents of the seeds of Peganum-harmala: Isolation and structure elucidation of two β-carbolines—harmalacinine and norharmine. Heterocycles. 1989;29:521–527. doi: 10.3987/COM-89-4834. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

