Development of A Chimeric Antigen Receptor Targeting C-Type Lectin-Like Molecule-1 for Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 29077054
- PMCID: PMC5713229
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18112259
Development of A Chimeric Antigen Receptor Targeting C-Type Lectin-Like Molecule-1 for Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
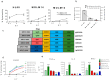
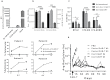
The treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with targeted immunotherapy is challenged by the heterogeneity of the disease and a lack of tumor-exclusive antigens. Conventional immunotherapy targets for AML such as CD33 and CD123 have been proposed as targets for chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T-cells (CAR-T-cells), a therapy that has been highly successful in the treatment of B-cell leukemia and lymphoma. However, CD33 and CD123 are present on hematopoietic stem cells, and targeting with CAR-T-cells has the potential to elicit long-term myelosuppression. C-type lectin-like molecule-1 (CLL1 or CLEC12A) is a myeloid lineage antigen that is expressed by malignant cells in more than 90% of AML patients. CLL1 is not expressed by healthy Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs), and is therefore a promising target for CAR-T-cell therapy. Here, we describe the development and optimization of an anti-CLL1 CAR-T-cell with potent activity on both AML cell lines and primary patient-derived AML blasts in vitro while sparing healthy HSCs. Furthermore, in a disseminated mouse xenograft model using the CLL1-positive HL60 cell line, these CAR-T-cells completely eradicated tumor, thus supporting CLL1 as a promising target for CAR-T-cells to treat AML while limiting myelosuppressive toxicity.
Keywords: AML; CAR-T-cell; CLL-1; hematopoiesis; optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rotiroti M.C., Arcangeli S., Casucci M., Perriello V., Bondanza A., Biondi A., Tettamanti S., Biagi E. Acute myeloid leukemia targeting by chimeric antigen receptor t cells: Bridging the gap from preclinical modeling to human studies. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017;28:231–241. doi: 10.1089/hum.2016.092. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buggins A.G., Milojkovic D., Arno M.J., Lea N.C., Mufti G.J., Thomas N.S., Hirst W.J. Microenvironment produced by acute myeloid leukemia cells prevents t cell activation and proliferation by inhibition of nf-kappab, c-myc, and prb pathways. J. Immunol. 2001;167:6021–6030. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.10.6021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pizzitola I., Anjos-Afonso F., Rouault-Pierre K., Lassailly F., Tettamanti S., Spinelli O., Biondi A., Biagi E., Bonnet D. Chimeric antigen receptors against cd33/cd123 antigens efficiently target primary acute myeloid leukemia cells in vivo. Leukemia. 2014;28:1596–1605. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.62. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

