Why do BCL-2 inhibitors work and where should we use them in the clinic?
- PMID: 29077093
- PMCID: PMC5729538
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2017.183
Why do BCL-2 inhibitors work and where should we use them in the clinic?
Abstract
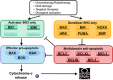
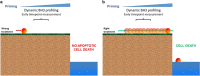
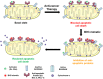
Intrinsic apoptosis is controlled by the BCL-2 family of proteins but the complexity of intra-family interactions makes it challenging to predict cell fate via standard molecular biology techniques. We discuss BCL-2 family regulation and how to determine cells' readiness for apoptosis and anti-apoptotic dependence. Cancer cells often adopt anti-apoptotic defense mechanisms in response to oncogenic stress or anti-cancer therapy. However, by determining their anti-apoptotic addiction, we can use novel BH3 mimetics to overwhelm this apoptotic blockade. We outline the development and uses of these unique anti-apoptotic inhibitors and how to possibly combine them with other anti-cancer agents using dynamic BH3 profiling (DBP) to improve personalized cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Green DR. Cell death and the immune system: getting to how and why. Immunol Rev 2017; 277: 4–8. - PubMed
-
- Zou H, Li Y, Liu X, Wang X. An APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 11549–11556. - PubMed
-
- McDonnell TJ, Korsmeyer SJ. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature 1991; 349: 254–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

