Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of meloxicam in Mediterranean buffalo calves (Bubalus bubalis)
- PMID: 29077759
- PMCID: PMC5659777
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187252
Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of meloxicam in Mediterranean buffalo calves (Bubalus bubalis)
Abstract
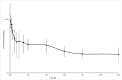
The aims of the investigation were to establish for the first time (i) clinical efficacy and (ii) pharmacokinetic profile of meloxicam intravenously (IV) administered in male Mediterranean buffalo calves after surgical orchiectomy. The study was performed on 10 healthy buffalo calves, between 4 and 5 months old and between 127 and 135 kg of body weight (b.w.). An IV injection of 0.5 mg/kg b.w. of meloxicam was administered in six calves (treated group, TG) immediately after surgery; the other four animals were used as untreated control group (CG). The clinical efficacy of meloxicam was evaluated pre- and post-surgery by monitoring respiratory rate (RR), heart rate (HR), rectal temperature (T°C), serum cortisol levels (SCL) and pain score (PS). Significant inter-groups differences were detected at sampling times (T): 4 hour (h) for RR (P<0.05), at T1-4-6-8 h for PS (P<0.05) and at T4-6-8 h for SCL (P < 0.0001). Regarding the mean intra-group values observed pre (T0) and post-surgery (from T15 min to T72 h), significant difference between the groups were found for RR (P<0.01), PS and SCL (P<0.05). The pharmacokinetic profile was best fitted by a two-compartmental model and characterized by a fast distribution half-life and slow elimination half-life (0.09 ± 0.06 h and 21.51 ± 6.4 h, respectively) and meloxicam mean concentrations at 96 h was of 0.18 ± 0.14 μg/mL. The volume of distribution and clearance values were quite low, but reasonably homogenous among individuals (Vdss 142.31 ± 55.08 mL/kg and ClB 4.38 ± 0.95 mL/kg/h, respectively). The IV administration of meloxicam in buffalo calves shows encouraging effects represented by significant and prolonged analgesic effects, significant reduction of SCL as well as similar pharmacokinetic profile to bovine calves.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- FAOSTAT, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation. 2014. Accessed May 15, 2016. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QA
-
- Zicarelli L. Influence of seasonality on buffalo production In: Presicce GA, Editor. The Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis)–Production and Research. Ed. Bentham Books; 2017. pp. 196–224.
-
- Giuffrida-Mendoza M, de Moreno A, Huerta-Leidenz N, Uzcátegui-Bracho S, Valero-Leal K, Romero S et al. Cholesterol and fatty acid composition of longissimus thoracis from water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) and Brahman-influenced cattle raised under savannah conditions. Meat Science. 2015; 106: 44–9. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2015.03.024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Voloski FL, Tonello L, Ramires T, Reta GG, Dewes C, Iglesias M et al. Influence of cutting and deboning operations on the microbiological quality and shelf life of buffalo meat. Meat Science. 2016; 116: 207–12. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.02.020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Repenning PE, Ahola JK, Callan RJ, Fox JT, French JT, Giles RL et al. Effects of pain mitigation and method of castration on behavior and feedlot performance in cull beef bulls. Journal of Animal Science. 2013; 91(10): 4975–83. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-6061 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

