PELI1 functions as a dual modulator of necroptosis and apoptosis by regulating ubiquitination of RIPK1 and mRNA levels of c-FLIP
- PMID: 29078411
- PMCID: PMC5692605
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1715742114
PELI1 functions as a dual modulator of necroptosis and apoptosis by regulating ubiquitination of RIPK1 and mRNA levels of c-FLIP
Abstract
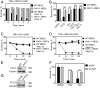
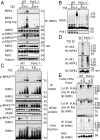
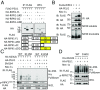
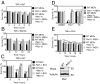
Apoptosis and necroptosis are two distinct cell death mechanisms that may be activated in cells on stimulation by TNFα. It is still unclear, however, how apoptosis and necroptosis may be differentially regulated. Here we screened for E3 ubiquitin ligases that could mediate necroptosis. We found that deficiency of Pellino 1 (PELI1), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, blocked necroptosis. We show that PELI1 mediates K63 ubiquitination on K115 of RIPK1 in a kinase-dependent manner during necroptosis. Ubiquitination of RIPK1 by PELI1 promotes the formation of necrosome and execution of necroptosis. Although PELI1 is not directly involved in mediating the activation of RIPK1, it is indispensable for promoting the binding of activated RIPK1 with its downstream mediator RIPK3 to promote the activation of RIPK3 and MLKL. Inhibition of RIPK1 kinase activity blocks PELI1-mediated ubiquitination of RIPK1 in necroptosis. However, we show that PELI1 deficiency sensitizes cells to both RIPK1-dependent and RIPK1-independent apoptosis as a result of down-regulated expression of c-FLIP, an inhibitor of caspase-8. Finally, we show that Peli1-/- mice are sensitized to TNFα-induced apoptosis. Thus, PELI1 is a key modulator of RIPK1 that differentially controls the activation of necroptosis and apoptosis.
Keywords: Peli1; TNF; apoptosis; necroptosis; ubiquitination.
Published under the PNAS license.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.Y. and D.R.G. were coauthors on a 2016 nomenclature paper. There was no collaboration between them.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Zinc finger protein 91 mediates necroptosis by initiating RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signal transduction in response to TNF receptor 1 ligation.Toxicol Lett. 2022 Mar 1;356:75-88. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.12.015. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Toxicol Lett. 2022. PMID: 34942311
-
Regulation of a distinct activated RIPK1 intermediate bridging complex I and complex II in TNFα-mediated apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jun 26;115(26):E5944-E5953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806973115. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29891719 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination of RIPK1 regulates its activation mediated by TNFR1 and TLRs signaling in distinct manners.Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 11;11(1):6364. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19935-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33311474 Free PMC article.
-
Necroptosis in development and diseases.Genes Dev. 2018 Mar 1;32(5-6):327-340. doi: 10.1101/gad.312561.118. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29593066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Holding RIPK1 on the Ubiquitin Leash in TNFR1 Signaling.Trends Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;26(6):445-461. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26877205 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of Zika Virus Infection.Annu Rev Pathol. 2023 Jan 24;18:181-203. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-031521-034739. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36151059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of RIPK3 in necroptosis, cell signaling, and disease.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Oct;54(10):1695-1704. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00868-z. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36224345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel necroptosis-related gene index for predicting prognosis and a cold tumor immune microenvironment in stomach adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:968165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968165. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired RIPK1 ubiquitination sensitizes mice to TNF toxicity and inflammatory cell death.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Mar;28(3):985-1000. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00629-3. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 32999468 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of necroptosis and perspectives for the development of new drugs preventing ischemic/reperfusion of cardiac injury.Apoptosis. 2022 Oct;27(9-10):697-719. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01760-x. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35986803 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

