In Vitro Seamless Stack Enzymatic Assembly of DNA Molecules Based on a Strategy Involving Splicing of Restriction Sites
- PMID: 29079784
- PMCID: PMC5660187
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14496-5
In Vitro Seamless Stack Enzymatic Assembly of DNA Molecules Based on a Strategy Involving Splicing of Restriction Sites
Abstract
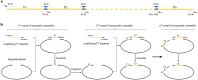
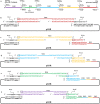
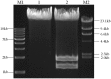
The standard binary enzymatic assembly, which operates by inserting one DNA fragment into a plasmid, has a higher assembly success rate than the polynary enzymatic assembly, which inserts two or more fragments into the plasmid. However, it often leaves a nucleotide scar at the junction site. When a large DNA molecule is assembled stepwise into a backbone plasmid in a random piecewise manner, the scars will damage the structure of the original DNA sequence in the final assembled plasmids. Here, we propose an in vitro Seamless Stack Enzymatic Assembly (SSEA) method, a novel binary enzymatic assembly method involving a seamless strategy of splicing restriction sites via a stepwise process of multiple enzymatic reactions that does not leave nucleotide scars at the junction sites. We have demonstrated the success and versatility of this method through the assembly of 1) a 4.98 kb DNA molecule in the 5' → 3' direction using BamHI to generate the sticky end of the assembly entrance, 2) a 7.09 kb DNA molecule in the 3' → 5' direction using SmaI to generate the blunt end of the assembly entrance, and 3) an 11.88 kb DNA molecule by changing the assembly entrance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[The effect of Z-conformation on enzymatic activity of restriction endonucleases].Mol Biol (Mosk). 1989 Nov-Dec;23(6):1638-44. Mol Biol (Mosk). 1989. PMID: 2561178 Russian.
-
[Plasmid vector for cloning, determination of nucleotide sequence and directed assembly of DNA fragments].Mol Biol (Mosk). 1987 Jan-Feb;21(1):194-9. Mol Biol (Mosk). 1987. PMID: 3033473 Russian.
-
AFEAP cloning: a precise and efficient method for large DNA sequence assembly.BMC Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 14;17(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12896-017-0394-x. BMC Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29137618 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of restriction enzyme's DNA sequence recognition by PUVA treatment.Photochem Photobiol. 2001 Aug;74(2):269-73. doi: 10.1562/0031-8655(2001)074<0269:ioreds>2.0.co;2. Photochem Photobiol. 2001. PMID: 11547565
-
A strategy for seamless cloning of large DNA fragments from Streptomyces.Biotechniques. 2015 Oct 1;59(4):193-4, 196, 198-200. doi: 10.2144/000114338. eCollection 2015 Oct. Biotechniques. 2015. PMID: 26458547
Cited by
-
UniClo: scarless hierarchical DNA assembly without sequence constraint.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jun 20;53(12):gkaf548. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf548. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40548934 Free PMC article.
-
A seamless and iterative DNA assembly method named PS-Brick and its assisted metabolic engineering for threonine and 1-propanol production.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Jul 15;12:180. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1520-x. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31338122 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic Digestion and Ligation-Mediated PCR Used for Flanking Sequence Walking.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 26;10(1):3434. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60411-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32103092 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

