Dimethylguanidino valeric acid is a marker of liver fat and predicts diabetes
- PMID: 29083323
- PMCID: PMC5707166
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI95995
Dimethylguanidino valeric acid is a marker of liver fat and predicts diabetes
Abstract
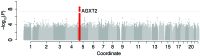
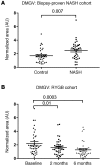
Unbiased, "nontargeted" metabolite profiling techniques hold considerable promise for biomarker and pathway discovery, in spite of the lack of successful applications to human disease. By integrating nontargeted metabolomics, genetics, and detailed human phenotyping, we identified dimethylguanidino valeric acid (DMGV) as an independent biomarker of CT-defined nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in the offspring cohort of the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) participants. We verified the relationship between DMGV and early hepatic pathology. Specifically, plasma DMGV levels were correlated with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in a hospital cohort of individuals undergoing gastric bypass surgery, and DMGV levels fell in parallel with improvements in post-procedure cardiometabolic parameters. Further, baseline DMGV levels independently predicted future diabetes up to 12 years before disease onset in 3 distinct human cohorts. Finally, we provide all metabolite peak data consisting of known and unidentified peaks, genetics, and key metabolic parameters as a publicly available resource for investigations in cardiometabolic diseases.
Keywords: Cardiology; Diabetes; Diagnostics; Metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chalasani N, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55(6):2005–2023. doi: 10.1002/hep.25762. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

