Population Pharmacokinetics of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole in Infants and Children
- PMID: 29084742
- PMCID: PMC5740321
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01813-17
Population Pharmacokinetics of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole in Infants and Children
Abstract
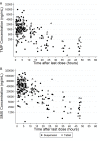
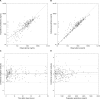
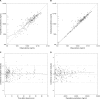
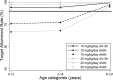
Trimethoprim (TMP)-sulfamethoxazole (SMX) is used to treat various types of infections, including community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) and Pneumocystis jirovecii infections in children. Pharmacokinetic (PK) data for infants and children are limited, and the optimal dosing is not known. We performed a multicenter, prospective PK study of TMP-SMX in infants and children. Separate population PK models were developed for TMP and SMX administered by the enteral route using nonlinear mixed-effects modeling. Optimal dosing was determined on the basis of the matching adult TMP exposure and attainment of the surrogate pharmacodynamic (PD) target for efficacy, a free TMP concentration above the MIC over 50% of the dosing interval. Data for a total of 153 subjects (240 samples for PK analysis) with a median postnatal age of 8 years (range, 0.1 to 20 years) contributed to the analysis for both drugs. A one-compartment model with first-order absorption and elimination characterized the TMP and SMX PK data well. Weight was included in the base model for clearance (CL/F) and volume of distribution (V/F). Both TMP and SMX CL/F increased with age. In addition, TMP and SMX CL/F were inversely related to the serum creatinine and albumin concentrations, respectively. The exposure achieved in children after oral administration of TMP-SMX at 8/40 mg/kg of body weight/day divided into administration every 12 h matched the exposure achieved in adults after administration of TMP-SMX at 320/1,600 mg/day divided into administration every 12 h and achieved the PD target for bacteria with an MIC of 0.5 mg/liter in >90% of infants and children. The exposure achieved in children after oral administration of TMP-SMX at 12/60 and 15/75 mg/kg/day divided into administration every 12 h matched the exposure achieved in adults after administration of TMP-SMX at 640/3,200 mg/day divided into administration every 12 h in subjects 6 to <21 years and 0 to <6 years of age, respectively, and was optimal for bacteria with an MIC of up to 1 mg/liter.
Keywords: children; infants; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; pharmacokinetics; sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Scientific Inc AR. 2013. Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim) package insert. Scientific Inc AR, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Iwamoto M, Mu Y, Lynfield R, Bulens SN, Nadle J, Aragon D, Petit S, Ray SM, Harrison LH, Dumyati G, Townes JM, Schaffner W, Gorwitz RJ, Lessa FC. 2013. Trends in invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Pediatrics 132:e817–e824. doi:10.1542/peds.2013-1112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, Rybak JM, Talan DA, Chambers HF. 2011. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children: executive summary. Clin Infect Dis 52:285–292. doi:10.1093/cid/cir034. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

