Repurposing metformin as a quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 29085409
- PMCID: PMC5656202
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v17i3.24
Repurposing metformin as a quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
Background: Quorum sensing is a mechanism of intercellular communication that controls the production of virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Inhibition of quorum sensing can disarm the virulence factors without exerting stress on bacterial growth that leads to emergence of antibiotic resistance.
Objectives: Finding a new quorum sensing inhibitor and determining its inhibitory activities against virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 strain.
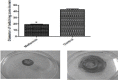
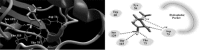
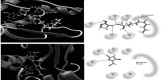
Methods: Quorum sensing was evaluated by estimation of violacein production by Chromobacterium violaceum CV026. Molecular docking was used to investigate the possible binding of metformin to LasR and rhlR receptors. The inhibition of pyocyanin, hemolysin, protease, elastase in addition to swimming and twitching motilities, biofilm formation and resistance to oxidative stress by metformin was also assessed.
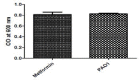
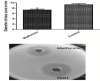
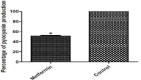
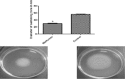
Results: Metformin significantly reduced the production of violacein pigment. Significant inhibition of pyocyanin, hemolysin, protease and elastase was achieved. Metformin markedly decreased biofilm formation, swimming and twitching motilities and increased the sensitivity to oxidative stress. In the molecular docking study, metformin could bind to LasR by hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interaction and to rhlR by hydrogen bonding only.
Conclusion: Metformin can act as a quorum sensing inhibitor and virulence inhibiting agent that may be useful in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.
Keywords: Metformin; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; quorum sensing; virulence inhibition.
Figures






References
-
- Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, et al. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature. 2000;406:959–964. - PubMed
-
- Driscoll JA, Brody SL, Kollef MH. The epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs. 2007;67:351–368. - PubMed
-
- Gellatly SL, Hancock RE. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: new insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathogens and Disease. 2013;67:159–173. - PubMed
-
- Fernebro J. Fighting bacterial infections - future treatment options. Drug Resistance Updates. 2011;14:125–139. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
