Heroin Contaminated with Fentanyl Dramatically Enhances Brain Hypoxia and Induces Brain Hypothermia
- PMID: 29085909
- PMCID: PMC5661359
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0323-17.2017
Heroin Contaminated with Fentanyl Dramatically Enhances Brain Hypoxia and Induces Brain Hypothermia
Abstract
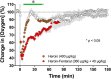
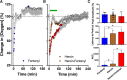
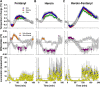
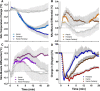
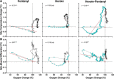
While opioid abuse is an established medical and public health issue, the increased availability of highly potent synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl, has given rise to acute health complications, including a comatose state and death during drug overdose. Since respiratory depression that leads to acute hypoxia is the most dangerous complication of opioid drug use, we examined the effects of intravenous heroin and heroin contaminated with 10% fentanyl on oxygen levels in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) monitored using high-speed amperometry in freely moving rats. Additionally, we examined the effects of heroin, fentanyl, and their mixture on locomotion and temperatures in the NAc, temporal muscle, and skin. Both fentanyl and heroin at human-relevant doses (400 and 40 μg/kg, respectively) induced rapid, strong and transient decreases in NAc oxygen, indicative of brain hypoxia. When the heroin-fentanyl mixture was injected, the NAc hypoxic response was greatly potentiated in its duration, suggesting sustained hypoxia. In contrast to modest, monophasic brain temperature increases caused by heroin alone, the heroin-fentanyl mixture induced a biphasic temperature response, with a prominent postinjection decrease resulting from peripheral vasodilation. This hypothermic effect, albeit much smaller and more transient, was typical of fentanyl injected alone. Our findings indicate that accidental use of fentanyl instead of heroin, or even a relatively minor contamination of "street heroin" with fentanyl, poses great danger for acute health complications, including a comatose state and death.
Keywords: brain temperature; metabolic activation; opioid; oxygen; vasoconstriction; vasodilation.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
