A review of phytochemistry, metabolite changes, and medicinal uses of the common sunflower seed and sprouts (Helianthus annuus L.)
- PMID: 29086881
- PMCID: PMC5622016
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-017-0328-7
A review of phytochemistry, metabolite changes, and medicinal uses of the common sunflower seed and sprouts (Helianthus annuus L.)
Abstract
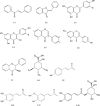
The sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) seed and sprout is a ubiquitous crop with abundant nutrients and biological activities. This review summarizes the nutritional and medical importance currently recognized but under-researched concerning both seed and sprout highlighting the potential benefits of their phytochemical constituents including phenolic acids, flavonoids and tocopherols. Furthermore, the dynamic metabolite changes which occur during germination and biological activities are evaluated. The aim is to provide scientific evidence for improving the dietary and pharmaceutical applications of this common but popular crop as a functional food.
Keywords: Biological activities; Chemical constituents; Metabolites; Nutritive value; Sunflower seeds.
Figures
References
-
- Prolea . De la production à la consommation. Statistiques desOléagineux et Protéagineux. Paris: Prolea Documentation; 2012. p. 48.
-
- Fowler MW. Plants, medicines and man. J Sci Food Agric. 2006;86(12):1797–1804. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2598. - DOI
-
- Bashir T, Mashwani ZR, Zahara K, Haider S, Mudrikah TS. Chemistry, pharmacology and ethnomedicinal uses of Helianthus annuus (sunflower): a review. Pure Appl Biol. 2015;4(2):226–235. doi: 10.19045/bspab.2015.42011. - DOI
-
- Alagawany M, Farag MR, Abd El-Hack ME, Dhama K. The practical application of sunflower meal in poultry nutrition. Adv Anim Vet Sci. 2015;3:634–648. doi: 10.14737/journal.aavs/2015/3.12.634.648. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

