Inhibition of curli assembly and Escherichia coli biofilm formation by the human systemic amyloid precursor transthyretin
- PMID: 29087319
- PMCID: PMC5699053
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1708805114
Inhibition of curli assembly and Escherichia coli biofilm formation by the human systemic amyloid precursor transthyretin
Abstract
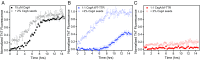
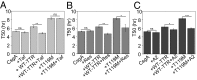
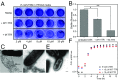
During biofilm formation, Escherichia coli and other Enterobacteriaceae produce an extracellular matrix consisting of curli amyloid fibers and cellulose. The precursor of curli fibers is the amyloidogenic protein CsgA. The human systemic amyloid precursor protein transthyretin (TTR) is known to inhibit amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation in vitro and suppress the Alzheimer's-like phenotypes in a transgenic mouse model of Aβ deposition. We hypothesized that TTR might have broad antiamyloid activity because the biophysical properties of amyloids are largely conserved across species and kingdoms. Here, we report that both human WT tetrameric TTR (WT-TTR) and its engineered nontetramer-forming monomer (M-TTR, F87M/L110M) inhibit CsgA amyloid formation in vitro, with M-TTR being the more efficient inhibitor. Preincubation of WT-TTR with small molecules that occupy the T4 binding site eliminated the inhibitory capacity of the tetramer; however, they did not significantly compromise the ability of M-TTR to inhibit CsgA amyloidogenesis. TTR also inhibited amyloid-dependent biofilm formation in two different bacterial species with no apparent bactericidal or bacteriostatic effects. These discoveries suggest that TTR is an effective antibiofilm agent that could potentiate antibiotic efficacy in infections associated with significant biofilm formation.
Keywords: CsgA; amyloids; biofilms; curli; transthyretin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284:1318–1322. - PubMed
-
- Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:95–108. - PubMed
-
- Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P. Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13:34–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

