A vimentin binding small molecule leads to mitotic disruption in mesenchymal cancers
- PMID: 29087350
- PMCID: PMC5699095
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1716009114
A vimentin binding small molecule leads to mitotic disruption in mesenchymal cancers
Abstract
Expression of the transcription factor FOXC2 is induced and necessary for successful epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a developmental program that when activated in cancer endows cells with metastatic potential and the properties of stem cells. As such, identifying agents that inhibit the growth of FOXC2-transformed cells represents an attractive approach to inhibit chemotherapy resistance and metastatic dissemination. From a high throughput synthetic lethal screen, we identified a small molecule, FiVe1, which selectively and irreversibly inhibits the growth of mesenchymally transformed breast cancer cells and soft tissue sarcomas of diverse histological subtypes. FiVe1 targets the intermediate filament and mesenchymal marker vimentin (VIM) in a mode which promotes VIM disorganization and phosphorylation during metaphase, ultimately leading to mitotic catastrophe, multinucleation, and the loss of stemness. These findings illustrate a previously undescribed mechanism for interrupting faithful mitotic progression and may ultimately inform the design of therapies for a broad range of mesenchymal cancers.
Keywords: cancer stem cell; drug discovery; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; mitosis; vimentin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.J.B., S.A.M., P.G.S., and L.L.L. are listed as inventors on a patent application related to the small molecules described in this manuscript.
Figures

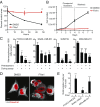

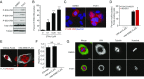
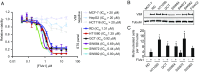
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

