Evaluation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-TiC Metal Matrix Composite Prepared by Conventional, Microwave and Spark Plasma Sintering Methods
- PMID: 29088114
- PMCID: PMC5706202
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10111255
Evaluation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-TiC Metal Matrix Composite Prepared by Conventional, Microwave and Spark Plasma Sintering Methods
Abstract
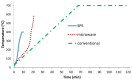
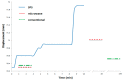
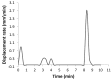
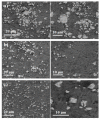
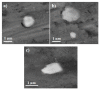
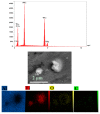
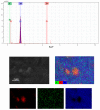
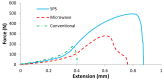
In this research, the mechanical properties and microstructure of Al-15 wt % TiC composite samples prepared by spark plasma, microwave, and conventional sintering were investigated. The sintering process was performed by the speak plasma sintering (SPS) technique, microwave and conventional furnaces at 400 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C, respectively. The results showed that sintered samples by SPS have the highest relative density (99% of theoretical density), bending strength (291 ± 12 MPa), and hardness (253 ± 23 HV). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) investigations showed the formation of TiO₂ from the surface layer decomposition of TiC particles. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs demonstrated uniform distribution of reinforcement particles in all sintered samples. The SEM/EDS analysis revealed the formation of TiO₂ around the porous TiC particles.
Keywords: aluminum; microwave; spark plasma sintering; titanium carbide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigation on in-situ formed Al3V-Al-VC nano composite through conventional, microwave and spark plasma sintering.Heliyon. 2019 May 21;5(5):e01754. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01754. eCollection 2019 May. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31193508 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of Mechanically Alloyed Ni-TiC Composites Processed via Spark Plasma Sintering.Materials (Basel). 2020 Nov 23;13(22):5306. doi: 10.3390/ma13225306. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33238641 Free PMC article.
-
Semisolid State Sintering Behavior of Aluminum⁻Stainless Steel 316L Composite Materials by Powder Metallurgy.Materials (Basel). 2019 May 7;12(9):1473. doi: 10.3390/ma12091473. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31067717 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Graphene Nanosheets Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Titanium Matrix Composite Produced by Cold Pressing and Sintering.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 Dec 8;8(12):1024. doi: 10.3390/nano8121024. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30544792 Free PMC article.
-
On the Non-Thermal Mechanisms in Microwave Sintering of Materials.Materials (Basel). 2025 Feb 3;18(3):668. doi: 10.3390/ma18030668. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of Electricity Transmission Conductors: Challenges and Remedies.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;15(22):8094. doi: 10.3390/ma15228094. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36431580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties of WCCo Composites Produced by the SPS Method Intended for Cutting Tools for Machining of Wood-Based Materials.Materials (Basel). 2021 May 17;14(10):2618. doi: 10.3390/ma14102618. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067915 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles' Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 Aug 10;8(8):610. doi: 10.3390/nano8080610. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30103408 Free PMC article.
-
Phase stability and microstructural properties of high entropy alloy reinforced aluminium matrix composites consolidated via spark plasma sintering.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 14;10(2):e24498. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24498. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38298639 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation on in-situ formed Al3V-Al-VC nano composite through conventional, microwave and spark plasma sintering.Heliyon. 2019 May 21;5(5):e01754. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01754. eCollection 2019 May. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31193508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shin J.H., Choi H.J., Bae D.H. The structure and properties of 2024 aluminum composites reinforced with TiO 2 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2014;607:605–610. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.04.038. - DOI
-
- Torralba J., da Costa C., Velasco F. P/M aluminum matrix composites: An overview. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003;133:203–206. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00234-0. - DOI
-
- Ghasali E., Yazdani-rad R., Asadian K., Ebadzadeh T. Production of Al-SiC-TiC hybrid composites using pure and 1056 aluminum powders prepared through microwave and conventional heating methods. J. Alloys Compd. 2017;690:512–518. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.145. - DOI
-
- Ghasali E., Alizadeh M., Ebadzadeh T., Pakseresht A.H., Rahbari A. Investigation on microstructural and mechanical properties of B4C–aluminum matrix composites prepared by microwave sintering. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015;4:411–415. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2015.02.005. - DOI
-
- Das T., Munroe P., Bandyopadhyay S. The effect of Al 2 O 3 particulates on the precipitation behaviour of 6061 aluminium-matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1996;31:5351–5361. doi: 10.1007/BF01159304. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

