Development of an interstitial cystitis risk score for bladder permeability
- PMID: 29088231
- PMCID: PMC5663335
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185686
Development of an interstitial cystitis risk score for bladder permeability
Abstract
Background: Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC) is a multifactorial syndrome of severe pelvic and genitalia pain and compromised urinary function; a subset of IC patients present with Hunner's lesions or ulcers on their bladder walls (UIC). UIC is diagnosed by cystoscopy, which may be quite painful. The objective of this study was to determine if a calculated Bladder Permeability Defect Risk Score (BP-RS) based on non-invasive urinary cytokines could discriminate UIC patients from controls and IC patients without Hunner's ulcers.
Methods: A national crowdsourcing effort targeted IC patients and age-matched controls to provide urine samples. Urinary cytokine levels for GRO, IL-6, and IL-8 were determined using a Luminex assay.
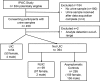
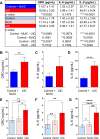
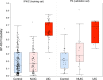
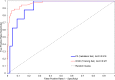
Results: We collected 448 urine samples from 46 states consisting of 153 IC patients (147 female, 6 male), of which 54 UIC patients (50 females, 4 male), 159 female controls, and 136 male controls. A defined BP-RS was calculated to classify UIC, or a bladder permeability defect etiology, with 89% validity.
Conclusions: The BP-RS Score quantifies UIC risk, indicative of a bladder permeability defect etiology in a subset of IC patients. The Bladder Permeability Defect Risk Score is the first validated urine biomarker assay for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating symptom severity and urinary cytokine levels in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patients, with and without Hunner's lesions.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2024 Apr 15;12(2):110-118. doi: 10.62347/BLED2401. eCollection 2024. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2024. PMID: 38736620 Free PMC article.
-
Crowdsourcing Disease Biomarker Discovery Research: The IP4IC Study.J Urol. 2018 May;199(5):1344-1350. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.09.167. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29225061
-
Symptom profile variability of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome by age.BJU Int. 2012 May;109(9):1356-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10481.x. Epub 2011 Aug 24. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 21883848
-
The role of the bladder surface in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome.Can J Urol. 2007 Aug;14(4):3599-607. Can J Urol. 2007. PMID: 17784979 Review.
-
Non-Hunner's Interstitial Cystitis Is Different from Hunner's Interstitial Cystitis and May Be Curable by Uterosacral Ligament Repair.Urol Int. 2022;106(7):649-657. doi: 10.1159/000524321. Epub 2022 May 5. Urol Int. 2022. PMID: 35512665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered Angiogenic Growth Factors in Urine of Prostate Cancer Survivors With Radiation History and Radiation Cystitis.Urology. 2018 Oct;120:180-186. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2018.07.025. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Urology. 2018. PMID: 30059715 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of deep phenotyping features of UCPPS with and without Hunner lesion: A MAPP-II Research Network Study.Neurourol Urodyn. 2021 Mar;40(3):810-818. doi: 10.1002/nau.24623. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021. PMID: 33604963 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome (IC/BPS) Diagnosis: A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Methodologies.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 5;14(23):2734. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232734. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682641 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-Analysis of COVID-19 Metabolomics Identifies Variations in Robustness of Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 21;24(18):14371. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814371. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762673 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating symptom severity and urinary cytokine levels in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patients, with and without Hunner's lesions.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2024 Apr 15;12(2):110-118. doi: 10.62347/BLED2401. eCollection 2024. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2024. PMID: 38736620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clemens JQ, Mullins C, Kusek JW, Kirkali Z, Mayer EA, Rodriguez LV, et al. The MAPP research network: a novel study of urologic chronic pelvic pain syndromes. BMC urology. 2014;14:57 doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-14-57 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4134515. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berry SH, Elliott MN, Suttorp M, Bogart LM, Stoto MA, Eggers P, et al. Prevalence of symptoms of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis among adult females in the United States. J Urol. 2011;186(2):540–4. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.03.132 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3513327. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Suskind AM, Berry SH, Ewing BA, Elliott MN, Suttorp MJ, Clemens JQ. The prevalence and overlap of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men: results of the RAND Interstitial Cystitis Epidemiology male study. The Journal of urology. 2013;189(1):141–5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.088 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3894747. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hurst RE, Meerveld BG, Wisniewski AB, VanGordon S, Lin H, Kropp BP, et al. Increased bladder permeability in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Transl Androl Urol. 2015;4(5):563–71. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.10.03 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4706376. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

