Cell-free circulating tumor DNA analysis for breast cancer and its clinical utilization as a biomarker
- PMID: 29088906
- PMCID: PMC5650461
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20608
Cell-free circulating tumor DNA analysis for breast cancer and its clinical utilization as a biomarker
Abstract
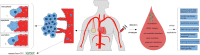
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the blood of cancer patients contains much information on genetic and epigenetic profiles associated with cancer development, progression, and response to therapy. Analysis of ctDNA provides an opportunity for non-invasive sampling of tumor DNA repetitiously and therefore advance precision medicine. Recent development in massively parallel sequencing and digital genomic techniques support the analytical and clinical validity of ctDNA as a promising 'liquid biopsy' in human cancer. In this review, we discussed the current status of cell-free ctDNA including ctDNA biology, recently developed techniques for ctDNA detection, breast cancer specific detecting strategies, with a focus on clinical applications of ctDNA-based biomarkers in breast oncology.
Keywords: biomarker; breast cancer; ctDNA; liquid biopsy.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Goding Sauer A, Kramer JL, Smith RA, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2015: Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2016;66:31–42. - PubMed
-
- Massihnia D, Perez A, Bazan V, Bronte G, Castiglia M, Fanale D, Barraco N, Cangemi A, Di Piazza F, Calo V, Rizzo S, Cicero G, Pantuso G, et al. A headlight on liquid biopsies: a challenging tool for breast cancer management. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:4263–4273. - PubMed
-
- Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS, Pantel K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:426–437. - PubMed
-
- Mandel P, Métais P. [Les acides nucléiques du plasma sanguin chez l’homme.][Article in undetermined language] C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1948;142:241–243. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

