Implementation of sepsis bundles in public hospitals in Brazil: a prospective study with heterogeneous results
- PMID: 29089025
- PMCID: PMC5664817
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1858-z
Implementation of sepsis bundles in public hospitals in Brazil: a prospective study with heterogeneous results
Abstract
Background: Public hospitals in emerging countries pose a challenge to quality improvement initiatives in sepsis. Our objective was to evaluate the results of a quality improvement initiative in sepsis in a network of public institutions and to assess potential differences between institutions that did or did not achieve a reduction in mortality.
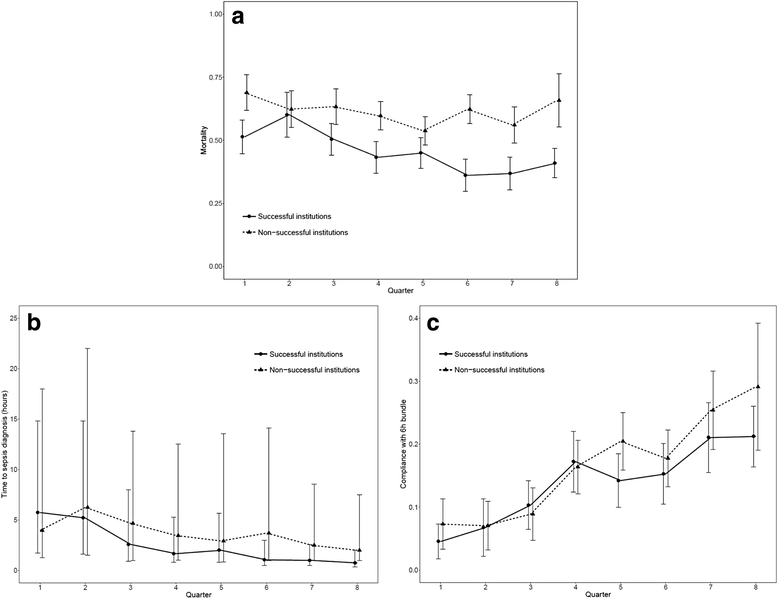
Methods: We conducted a prospective study of patients with sepsis or septic shock. We collected baseline data on compliance with the Surviving Sepsis Campaign 6-h bundles and mortality. Afterward, we initiated a multifaceted quality improvement initiative for patients with sepsis or septic shock in all hospital sectors. The primary outcome was hospital mortality over time. The secondary outcomes were the time to sepsis diagnosis and compliance with the entire 6-h bundles throughout the intervention. We defined successful institutions as those where the mortality rates decreased significantly over time, using a logistic regression model. We analyzed differences over time in the secondary outcomes by comparing the successful institutions with the nonsuccessful ones. We assessed the predictors of in-hospital mortality using logistic regression models. All tests were two-sided, and a p value less than 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
Results: We included 3435 patients from the emergency departments (50.7%), wards (34.1%), and intensive care units (15.2%) of 9 institutions. Throughout the intervention, there was an overall reduction in the risk of death, in the proportion of septic shock, and the time to sepsis diagnosis, as well as an improvement in compliance with the 6-h bundle. The time to sepsis diagnosis, but not the compliance with bundles, was associated with a reduction in the risk of death. However, there was a significant reduction in mortality in only two institutions. The reduction in the time to sepsis diagnosis was greater in the successful institutions. By contrast, the nonsuccessful sites had a greater increase in compliance with the 6-h bundle.
Conclusions: Quality improvement initiatives reduced sepsis mortality in public Brazilian institutions, although not in all of them. Early recognition seems to be a more relevant factor than compliance with the 6-h bundle.
Keywords: Bundles; Developing countries; Sepsis; Septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research and ethics committee of Universidade Federal de São Paulo approved the study (number 1387/10) and waived the need for informed consent because of the nature of the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

