Left Atrial Volume and Mortality in Patients With Aortic Stenosis
- PMID: 29089338
- PMCID: PMC5721760
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006615
Left Atrial Volume and Mortality in Patients With Aortic Stenosis
Abstract
Background: Left atrium (LA) enlargement is common in patients with aortic stenosis (AS), yet its prognostic implications are unclear. This study investigates the value of left atrial volume (LAV) and LAV normalized to body size for predicting mortality in AS.
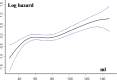
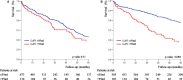
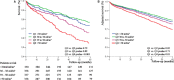
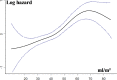
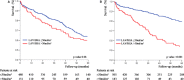
Methods and results: We included 1351 patients with AS in sinus rhythm at diagnosis and analyzed the occurrence of all-cause death during follow-up with medical and surgical management. Five parameters of LA enlargement were tested: nonindexed LAV and normalized LAV by ratiometric (LAV/body surface area [BSA] and LAV/height) and allometric (LAV/BSA1.7 and LAV/height2.0) scaling. For each parameter, patients in the highest quartile were at high risk of death, whereas outcome was better and similar for the other quartiles. Five-year survival was lower for patients with LAV >95 mL and LAV/BSA >50 mL/m2 compared with those with no or mild LA enlargement (both P<0.001). After adjustment for established outcome predictors, including surgery, high risk of death was observed with LAV >95 mL (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.40 [95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.88]) and LAV/BSA >50 mL/m2 (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.42 [95% confidence interval, 1.08-1.91]). LAV/BSA and LAV showed good and similar predictive performance, whereas other scaling methods did not show better outcome prediction. In patients with severe AS at baseline, preserved (≥50%) ejection fraction, and no or minimal symptoms, LA enlargement was significantly associated with mortality (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.87 [95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.44] for LAV >95 mL, and adjusted hazard ratio, 1.90 [95% confidence interval, 1.03-3.56] for LAV/BSA >50 mL/m2).
Conclusions: LA enlargement is an important predictor of mortality in AS, incrementally to known predictors of outcome. LAV and LAV/BSA have comparable predictive performance and should be assessed in clinical practice for risk stratification.
Keywords: aortic valve stenosis; echocardiography; left atrial volume index; normalization; outcome.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures

References
-
- Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP III, Guyton RA, O'Gara PT, Ruiz CE, Skubas NJ, Sorajja P, Sundt TM III, Thomas JD. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:2438–2488. - PubMed
-
- Vahanian A, Alfieri O, Andreotti F, Antunes MJ, Barón‐Esquivias G, Baumgartner H, Borger MA, Carrel TP, De Bonis M, Evangelista A, Falk V, Iung B, Lancellotti P, Pierard L, Price S, Schäfers HJ, Schuler G, Stepinska J, Swedberg K, Takkenberg J, Von Oppell UO, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Zembala M. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease (version 2012). Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2451–2496. - PubMed
-
- Otto CM. Valvular aortic stenosis: disease severity and timing of intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:2141–2151. - PubMed
-
- Mihaljevic T, Nowicki ER, Rajeswaran J, Blackstone EH, Lagazzi L, Thomas J, Lytle BW, Cosgrove DM. Survival after valve replacement for aortic stenosis: implications for decision making. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135:1270–1278. - PubMed
-
- Beach JM, Mihaljevic T, Rajeswaran J, Marwick T, Edwards ST, Nowicki ER, Thomas J, Svensson LG, Griffin B, Gillinov AM, Blackstone EH. Ventricular hypertrophy and left atrial dilatation persist and are associated with reduced survival after valve replacement for aortic stenosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:362–369. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

