Belowground stressors and long-term seagrass declines in a historically degraded seagrass ecosystem after improved water quality
- PMID: 29089513
- PMCID: PMC5663742
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14044-1
Belowground stressors and long-term seagrass declines in a historically degraded seagrass ecosystem after improved water quality
Abstract
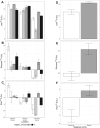
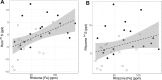
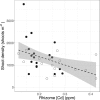
Continued seagrass declines in ecosystems with improved water quality may be driven by sediment stressors. One of the most cited examples of a seagrass ecosystem with declines is Cockburn Sound, Western Australia, where 75% of seagrasses (2169 ha) were lost in the 1960s-1980s due to poor water quality. Water quality has subsequently improved in Cockburn Sound, yet shoot density declines continue in some areas. Here, we investigated if sediment stressors (sulfide intrusion and heavy metals) contributed to declining Posidonia sinuosa shoot densities in Cockburn Sound. Seagrass δ34S were depleted at sites with a history of seagrass declines, indicating seagrasses at these sites were under sulfide stress. Heavy metals (Fe, Zn, Mn, Cr, Cu and Cd) in sediments and seagrasses did not show clear patterns with shoot density or biomass, and largely decreased from similar measurements in the late 1970s. However, seagrass cadmium concentrations were negatively correlated to seagrass biomass and shoot density. High cadmium concentrations interfere with sulfur metabolism in terrestrial plants, but impacts on seagrasses remain to be explored. Given that sulfide intrusion can prevent recolonization and drive seagrass declines, management plans in degraded seagrass ecosystems should include management of sediment stressors and water quality to provide comprehensive management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cambridge M, McComb A. The loss of seagrasses in Cockburn Sound, Western Australia. I. The time course and magnitude of seagrass decline in relation to industrial development. Aquatic Botany. 1984;20:229–243. doi: 10.1016/0304-3770(84)90089-5. - DOI
-
- Kendrick GA, et al. Changes in seagrass coverage in Cockburn Sound, Western Australia between 1967 and 1999. Aquatic Botany. 2002;73:75–87. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3770(02)00005-0. - DOI
-
- Pagès, A., Welsh, D. T., Robertson, D. & Panther, J. G. Diurnal shifts in co-distributions of sulfide and iron(II) and profiles of phosphate and ammonium in the rhizosphere of Zostera capricorni. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science (2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

