A signature of enhanced lipid metabolism, lipid peroxidation and aldehyde stress in therapy-induced senescence
- PMID: 29090099
- PMCID: PMC5661608
- DOI: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2017.75
A signature of enhanced lipid metabolism, lipid peroxidation and aldehyde stress in therapy-induced senescence
Abstract
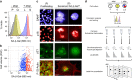
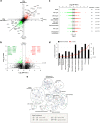
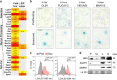
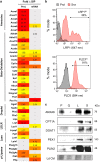
At their proliferative limit, normal cells arrest and undergo replicative senescence, displaying large cell size, flat morphology, and senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-β-Gal) activity. Normal or tumor cells exposed to genotoxic stress undergo therapy-induced senescence (TIS), displaying a similar phenotype. Senescence is considered a DNA damage response, but cellular heterogeneity has frustrated identification of senescence-specific markers and targets. To explore the senescent cell proteome, we treated tumor cells with etoposide and enriched SA-β-GalHI cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). The enriched TIS cells were compared to proliferating or quiescent cells by label-free quantitative LC-MS/MS proteomics and systems analysis, revealing activation of multiple lipid metabolism pathways. Senescent cells accumulated lipid droplets and imported lipid tracers, while treating proliferating cells with specific lipids induced senescence. Senescent cells also displayed increased lipid aldehydes and upregulation of aldehyde detoxifying enzymes. These results place deregulation of lipid metabolism alongside genotoxic stress as factors regulating cellular senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
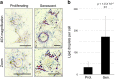
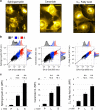

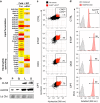
References
-
- Ma Y, Yang H, Pitt JM, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Therapy-induced microenvironmental changes in cancer. J Mol Med 2016; 94: 497–508. - PubMed
-
- Gewirtz DA. Autophagy and senescence in cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol 2014; 229: 6–9. - PubMed
-
- Falandry C, Bonnefoy M, Freyer G, Gilson E. Biology of cancer and aging: a complex association with cellular senescence. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 2604–2610. - PubMed
-
- Aravinthan A. Cellular senescence: a hitchhiker's guide. Human Cell 2015; 28: 51–64. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

