Management of Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fractures: Volar or Dorsal Locking Plate-Which Has Fewer Complications?
- PMID: 29091491
- PMCID: PMC5669324
- DOI: 10.1177/1558944716675129
Management of Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fractures: Volar or Dorsal Locking Plate-Which Has Fewer Complications?
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the functional outcomes and complications of volar and dorsal plating for the management of intra-articular distal radius fractures, with special regard to indications for dorsal plating. Furthermore, we examine the rationale for choosing dorsal plating and its frequency of use.
Methods: Clinical assessments included range of motion measurements at the wrist; grip strength; the Quick Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand score; and the Gartland and Werley score. Clinical results were compared with those achieved using a volarly placed locking plate system. According to Lutsky's plate theory, the rationale for choosing dorsal plating was based on 4 types of pathologic fractures.
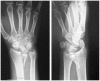
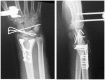
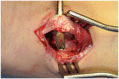
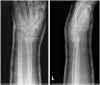
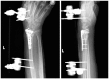
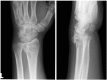
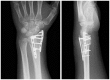
Results: Of 112 patients, 38 patients were treated with open reduction internal fixation via a dorsal approach and 68 patients were treated using a volar approach. Except for wrist flexion, there were no other statistical differences in the clinical results between groups for both subjective and objective parameters. There were no statistically significant differences in the complication rates between the volar and dorsal plated groups. One serious complication occurred after volar plating. The most common reason for choosing dorsal plating was irreducible dorsal die-punch fractures.
Conclusions: The treatment of displaced intra-articular distal radius fractures with a dorsally versus a volarly placed interlocking plate system demonstrated similar clinical results. Postoperative complications were not readily observed in the patients treated with a dorsal locking plate. Certain fracture patterns are more appropriately stabilized using a dorsal plate fixation.
Keywords: complications; distal radius fracture; dorsal approach; intra-articular fracture; locked plate fixation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Arora R, Lutz M, Hennerbichler A, et al. Complications following internal fixation of unstable distal radius fracture with a palmar locking-plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(5):316-322. - PubMed
-
- Benson EC, DeCarvalho A, Mikola EA, et al. Two potential causes of EPL rupture after distal radius volar plate fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;451:218-22. - PubMed
-
- Chou YC, Chen AC, Chen CY, et al. Dorsal and volar 2.4-mm titanium locking plate fixation for AO type C3 dorsally comminuted distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(6):974-981. - PubMed
-
- Gartland JJ, Jr, Werley CW. Evaluation of healed Colles’ fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1951;33(4):895-907. - PubMed
-
- Kamath AF, Zurakowski D, Day CS. Low-profile dorsal plating for dorsally angulated distal radius fractures: an outcomes study. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31(7):1061-1067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

