Identification of two types of GGAA-microsatellites and their roles in EWS/FLI binding and gene regulation in Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 29091716
- PMCID: PMC5665490
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186275
Identification of two types of GGAA-microsatellites and their roles in EWS/FLI binding and gene regulation in Ewing sarcoma
Abstract
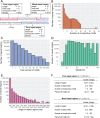
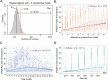
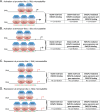
Ewing sarcoma is a bone malignancy of children and young adults, frequently harboring the EWS/FLI chromosomal translocation. The resulting fusion protein is an aberrant transcription factor that uses highly repetitive GGAA-containing elements (microsatellites) to activate and repress thousands of target genes mediating oncogenesis. However, the mechanisms of EWS/FLI interaction with microsatellites and regulation of target gene expression is not clearly understood. Here, we profile genome-wide protein binding and gene expression. Using a combination of unbiased genome-wide computational and experimental analysis, we define GGAA-microsatellites in a Ewing sarcoma context. We identify two distinct classes of GGAA-microsatellites and demonstrate that EWS/FLI responsiveness is dependent on microsatellite length. At close range "promoter-like" microsatellites, EWS/FLI binding and subsequent target gene activation is highly dependent on number of GGAA-motifs. "Enhancer-like" microsatellites demonstrate length-dependent EWS/FLI binding, but minimal correlation for activated and none for repressed targets. Our data suggest EWS/FLI binds to "promoter-like" and "enhancer-like" microsatellites to mediate activation and repression of target genes through different regulatory mechanisms. Such characterization contributes valuable insight to EWS/FLI transcription factor biology and clarifies the role of GGAA-microsatellites on a global genomic scale. This may provide unique perspective on the role of non-coding DNA in cancer susceptibility and therapeutic development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bailly RA, Bosselut R, Zucman J, Cormier F, Delattre O, Roussel M, et al. DNA-binding and transcriptional activation properties of the EWS-FLI-1 fusion protein resulting from the t(11;22) translocation in Ewing sarcoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14: 3230–41. Available: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=358690&tool=pm... - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lamber EP, Vanhille L, Textor LC, Kachalova GS, Sieweke MH, Wilmanns M. Regulation of the transcription factor Ets-1 by DNA-mediated homo-dimerization. EMBO J. 2008;27: 2006–17. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ohno T, Rao VN, Shyam E, Reddy P. EWS/Fli-1 Chimeric Protein Is a Transcriptional Activator. Cancer Res. 1993;53: 5859–5863. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen PH, Triche TJ. Gene fusions encoding chimaeric transcription factors in solid tumours. Semin Cancer Biol. 1996;7: 3–14. doi: 10.1006/scbi.1996.0002 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

