Lactobacillus reuteri suppresses E. coli O157:H7 in bovine ruminal fluid: Toward a pre-slaughter strategy to improve food safety?
- PMID: 29091926
- PMCID: PMC5665532
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187229
Lactobacillus reuteri suppresses E. coli O157:H7 in bovine ruminal fluid: Toward a pre-slaughter strategy to improve food safety?
Abstract
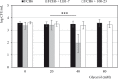
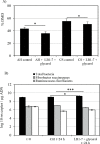
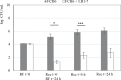
The bovine gastrointestinal tract (GIT) is the main reservoir for enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) responsible for food-borne infections. Therefore, it is crucial to develop strategies, such as EHEC suppression by antagonistic microorganisms, to reduce EHEC survival in the GIT of cattle and to limit shedding and food contamination. Most human-derived Lactobacillus reuteri strains produce hydroxypropionaldehyde (HPA), an antimicrobial compound, during anaerobic reduction of glycerol. The capacity of L. reuteri LB1-7, a strain isolated from raw bovine milk, to produce HPA and its antimicrobial activity against an O157:H7 EHEC strain (FCH6) were evaluated in bovine rumen fluid (RF) under strict anaerobiosis. EHEC was totally suppressed when incubated in RF inoculated with L. reuteri LB1-7 and supplemented with 80 mM glycerol (RF-Glyc80). The addition of LB1-7 or glycerol alone did not modify EHEC survival in RF. Glycerol was converted to HPA (up to 14 mM) by LB1-7 during incubation in RF-Glyc80, and HPA production appeared to be responsible for EHEC suppression. The bactericidal activity of L. reuteri LB1-7, the concentration of glycerol required and the level of HPA produced depended on physiological and ecological environments. In vitro experiments also showed that EHEC inoculated in rumen fluid and exposed to L. reuteri and glycerol had a very limited growth in rectal contents. However, L. reuteri exerted an antimicrobial activity against the rumen endogenous microbiota and perturbed feedstuff degradation in the presence of glycerol. The potential administration of L. reuteri and glycerol in view of application to finishing beef cattle at the time of slaughter is discussed. Further in vivo studies will be important to confirm the efficiency of L. reuteri and glycerol supplementation against EHEC shedding in ruminants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Law D. Virulence factors of Escherichia coli O157 and other Shiga toxin-producing E. coli. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2000; 88:729–745. - PubMed
-
- Caprioli A, Morabito S, Brugere H, Oswald E. Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli: emerging issues on virulence and modes of transmission. Veterinary Research. 2005; 36:289–311. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2005002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gaggìa F, Mattarelli P, Biavati B. Probiotics and prebiotics in animal feeding for safe food production. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 2010; 141 Suppl 1:S15–S28. - PubMed
-
- Bøhle LA, Brede DA, Diep DB, Holo H, Nes IF. Specific degradation of the mucus adhesion-promoting protein (MapA) of Lactobacillus reuteri to an antimicrobial peptide. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2010; 76:7306–7309. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01423-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

