Practice guideline: Cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential testing: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology
- PMID: 29093067
- PMCID: PMC5705249
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004690
Practice guideline: Cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential testing: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology
Abstract
Objective: To systematically review the evidence and make recommendations with regard to diagnostic utility of cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (cVEMP and oVEMP, respectively). Four questions were asked: Does cVEMP accurately identify superior canal dehiscence syndrome (SCDS)? Does oVEMP accurately identify SCDS? For suspected vestibular symptoms, does cVEMP/oVEMP accurately identify vestibular dysfunction related to the saccule/utricle? For vestibular symptoms, does cVEMP/oVEMP accurately and substantively aid diagnosis of any specific vestibular disorder besides SCDS?
Methods: The guideline panel identified and classified relevant published studies (January 1980-December 2016) according to the 2004 American Academy of Neurology process.
Results and recommendations: Level C positive: Clinicians may use cVEMP stimulus threshold values to distinguish SCDS from controls (2 Class III studies) (sensitivity 86%-91%, specificity 90%-96%). Corrected cVEMP amplitude may be used to distinguish SCDS from controls (2 Class III studies) (sensitivity 100%, specificity 93%). Clinicians may use oVEMP amplitude to distinguish SCDS from normal controls (3 Class III studies) (sensitivity 77%-100%, specificity 98%-100%). oVEMP threshold may be used to aid in distinguishing SCDS from controls (3 Class III studies) (sensitivity 70%-100%, specificity 77%-100%). Level U: Evidence is insufficient to determine whether cVEMP and oVEMP can accurately identify vestibular function specifically related to the saccule/utricle, or whether cVEMP or oVEMP is useful in diagnosing vestibular neuritis or Ménière disease. Level C negative: It has not been demonstrated that cVEMP substantively aids in diagnosing benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, or that cVEMP or oVEMP aids in diagnosing/managing vestibular migraine.
© 2017 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

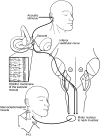
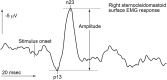

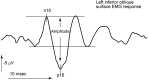
References
-
- Colebatch JG, Halmagyi GM. Vestibular evoked potentials in human neck muscles before and after unilateral vestibular differentiation. Neurology 1992;42:1635–1636. - PubMed
-
- Clarke AH. Laboratory testing of the vestibular system. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010;18:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Magliulo G, Gagliardi S, Appiani MC, Iannella G, Re M. Vestibular neurolabyrinthitis: a follow-up study with cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials and the video head impulse test. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2014;123:162–173. - PubMed
-
- Murofushi T. Clinical application of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP). Auris Nasus Larynx 2016;43:367–376. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
