Interaction of IL-6 and TNF-α contributes to endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mouse hearts
- PMID: 29095915
- PMCID: PMC5667841
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187189
Interaction of IL-6 and TNF-α contributes to endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mouse hearts
Abstract
Objectives: Inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), are individually considered as important contributors to endothelial dysfunction in obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D). However, their interactions in coronary arteriole endothelial dysfunction are uncertain. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the effects of TNF-α and IL-6 interactions on coronary endothelial dysfunction in experimental T2D.
Methods: The studies used wild type (WT), diabetic mice (db/db), db/db null for TNF (dbTNF-/dbTNF-), and db/db mice treated with neutralizing antibody to IL-6 (anti-IL-6). Endothelium-dependent (acetylcholine [ACh], or luminal flow-induced shear stress) and endothelium-independent (sodium nitroprusside [SNP]) vasodilation of isolated and pressurized coronary arterioles were determined. Quantitative PCR, Western blot, and immunofluorescence staining were utilized for mechanistic studies.
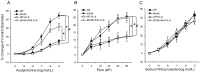
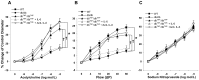
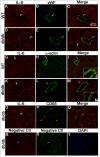
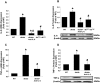
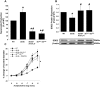
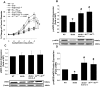
Results: Relative to WT, arteriolar dilation to both ACh and flow was attenuated in db/db mice and dbTNF-/dbTNF-. Treatment of dbTNF-/dbTNF- and db/db mice with anti-IL-6 improved arteriolar dilation compared to db/db mice. Immunofluorescence staining illustrated localization of IL-6 within the endothelial cells of coronary arterioles. In db/db mice, mRNA and protein expression of IL-6 and superoxide (O2-) production were higher, but reduced by anti-IL-6 treatment. Also, in db/db mice, mRNA and protein expression of TNF-α suppressed by the anti-IL-6 treatment and the reduced expression of mRNA and protein expression of IL-6 by the genetic deletion of TNF-α both supported a reciprocal regulation between TNF-α and IL-6. Superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) expression and phosphorylation of eNOS (p-eNOS/eNOS) were lower in db/db mice coronary arterioles and were restored in db/db+Anti-IL-6 and dbTNF-/dbTNF- mice.
Conclusion: The interactions between TNF-α and IL-6 exacerbate oxidative stress and reduce phosphorylation of eNOS, thereby contributing to coronary endothelial dysfunction in T2D mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB Sr., Larson MG, Massaro JM, Vasan RS. Predicting the 30-year risk of cardiovascular disease: the framingham heart study. Circulation. 2009;119(24):3078–84. Epub 2009/06/10. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.816694 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meigs JB. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: translation from population to prevention: the Kelly West award lecture 2009. Diabetes care. 2010;33(8):1865–71. Epub 2010/07/30. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0641 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vanhoutte PM. Endothelial dysfunction: the first step toward coronary arteriosclerosis. Circulation journal: official journal of the Japanese Circulation Society. 2009;73(4):595–601. Epub 2009/02/20. . - PubMed
-
- Cai H, Harrison DG. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circulation research. 2000;87(10):840–4. Epub 2000/11/14. . - PubMed
-
- Gamez-Mendez AM, Vargas-Robles H, Rios A, Escalante B. Oxidative Stress-Dependent Coronary Endothelial Dysfunction in Obese Mice. PloS one. 2015;10(9):e0138609 Epub 2015/09/19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138609 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

