Ghrelin as a Survival Hormone
- PMID: 29097101
- PMCID: PMC5777178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.10.001
Ghrelin as a Survival Hormone
Abstract
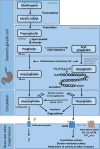
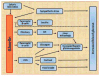
Ghrelin administration induces food intake and body weight gain. Based on these actions, the ghrelin system was initially proposed as an antiobesity target. Subsequent studies using genetic mouse models have raised doubts about the role of the endogenous ghrelin system in mediating body weight homeostasis or obesity. However, this is not to say that the endogenous ghrelin system is not important metabolically or otherwise. Here we review an emerging concept in which the endogenous ghrelin system serves an essential function during extreme nutritional and psychological challenges to defend blood glucose, protect body weight, avoid exaggerated depression, and ultimately allow survival.
Keywords: blood glucose; cachexia; ghrelin; hypoglycemia; psychosocial stress; survival.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
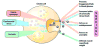
References
-
- Kojima M, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–660. - PubMed
-
- Howard AD, et al. A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science. 1996;273:974–977. - PubMed
-
- Wren AM, et al. Ghrelin causes hyperphagia and obesity in rats. Diabetes. 2001;50:2540–2547. - PubMed
-
- Tschop M, et al. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000;407:908–913. - PubMed
-
- Nakazato M, et al. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature. 2001;409:194–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

