Emerging role of angiogenesis in adaptive and maladaptive right ventricular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 29097426
- PMCID: PMC5900357
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00374.2017
Emerging role of angiogenesis in adaptive and maladaptive right ventricular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
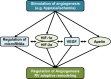
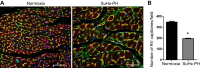
Right ventricular (RV) function is the primary prognostic factor for both morbidity and mortality in pulmonary hypertension (PH). RV hypertrophy is initially an adaptive physiological response to increased overload; however, with persistent and/or progressive afterload increase, this response frequently transitions to more pathological maladaptive remodeling. The mechanisms and disease processes underlying this transition are mostly unknown. Angiogenesis has recently emerged as a major modifier of RV adaptation in the setting of pressure overload. A novel paradigm has emerged that suggests that angiogenesis and angiogenic signaling are required for RV adaptation to afterload increases and that impaired and/or insufficient angiogenesis is a major driver of RV decompensation. Here, we summarize our current understanding of the concepts of maladaptive and adaptive RV remodeling, discuss the current literature on angiogenesis in the adapted and failing RV, and identify potential therapeutic approaches targeting angiogenesis in RV failure.
Figures

References
-
- Alastalo TP, Li M, Pde Jesus Perez V, Pham D, Sawada H, Wang JK, Koskenvuo M, Wang L, Freeman BA, Chang HY, Rabinovitch M. Disruption of PPARγ/β-catenin-mediated regulation of apelin impairs BMP-induced mouse and human pulmonary arterial EC survival. J Clin Invest 121: 3735–3746, 2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI43382. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alzoubi A, Toba M, Abe K, O’Neill KD, Rocic P, Fagan KA, McMurtry IF, Oka M. Dehydroepiandrosterone restores right ventricular structure and function in rats with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304: H1708–H1718, 2013. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00746.2012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

