EB1 and cytoplasmic dynein mediate protrusion dynamics for efficient 3-dimensional cell migration
- PMID: 29097501
- PMCID: PMC5893312
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201700444RR
EB1 and cytoplasmic dynein mediate protrusion dynamics for efficient 3-dimensional cell migration
Abstract
Microtubules have long been implicated to play an integral role in metastatic disease, for which a critical step is the local invasion of tumor cells into the 3-dimensional (3D) collagen-rich stromal matrix. Here we show that cell migration of human cancer cells uses the dynamic formation of highly branched protrusions that are composed of a microtubule core surrounded by cortical actin, a cytoskeletal organization that is absent in cells on 2-dimensional (2D) substrates. Microtubule plus-end tracking protein End-binding 1 and motor protein dynein subunits light intermediate chain 2 and heavy chain 1, which do not regulate 2D migration, critically modulate 3D migration by affecting RhoA and thus regulate protrusion branching through differential assembly dynamics of microtubules. An important consequence of this observation is that the commonly used cancer drug paclitaxel is 100-fold more effective at blocking migration in a 3D matrix than on a 2D matrix. This work reveals the central role that microtubule dynamics plays in powering cell migration in a more pathologically relevant setting and suggests further testing of therapeutics targeting microtubules to mitigate migration.-Jayatilaka, H., Giri, A., Karl, M., Aifuwa, I., Trenton, N. J., Phillip, J. M., Khatau, S., Wirtz, D. EB1 and cytoplasmic dynein mediate protrusion dynamics for efficient 3-dimensional cell migration.
Keywords: RhoA; microtubule; paclitaxel.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute Grants U54CA143868 and R01CA174388. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
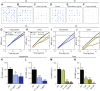
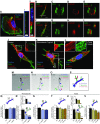
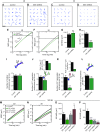
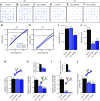

References
-
- Ridley A. J., Schwartz M. A., Burridge K., Firtel R. A., Ginsberg M. H., Borisy G., Parsons J. T., Horwitz A. R. (2003) Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302, 1704–1709 https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092053 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Raftopoulou M., Hall A. (2004) Cell migration: rho GTPases lead the way. Dev. Biol. 265, 23–32 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.06.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Machesky L. M., Way M. (1998) Actin branches out. Nature 394, 125–126 https://doi.org/10.1038/28039 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vladar E. K., Antic D., Axelrod J. D. (2009) Planar cell polarity signaling: the developing cell’s compass. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 1, a002964 https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a002964 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

