DnaJ Homolog Subfamily B Member 9 Is a Putative Autoantigen in Fibrillary GN
- PMID: 29097624
- PMCID: PMC5748922
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2017050566
DnaJ Homolog Subfamily B Member 9 Is a Putative Autoantigen in Fibrillary GN
Abstract
Fibrillary GN is a rare form of GN of uncertain pathogenesis that is characterized by the glomerular accumulation of randomly arranged, nonbranching fibrils (12-24 nm) composed of Ig and complement proteins. In this study, we used mass spectrometry to comprehensively define the glomerular proteome in fibrillary GN compared with that in controls and nonfibrillary GN renal diseases. We isolated glomeruli from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded biopsy specimens using laser capture microdissection and analyzed them with liquid chromatography and data-dependent tandem mass spectrometry. These studies identified DnaJ homolog subfamily B member 9 (DNAJB9) as a highly sampled protein detected only in fibrillary GN cases. The glomerular proteome of fibrillary GN cases also contained IgG1 as the dominant Ig and proteins of the classic complement pathway. In fibrillary GN specimens only, immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry with an anti-DNAJB9 antibody showed strong and specific staining of the glomerular tufts in a distribution that mimicked that of the immune deposits. Our results identify DNAJB9 as a putative autoantigen in fibrillary GN and suggest IgG1 and classic complement effector pathways as likely mediators of the destructive glomerular injury in this disease.
Keywords: Fibrillary glomerulonephritis; autoantigen; immunohistochemistry; mass spectrometry; renal biopsy.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

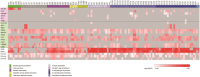
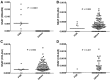


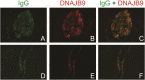
Comment in
-
Glomerular Disease Pathology in the Era of Proteomics: From Pattern to Pathogenesis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Jan;29(1):2-4. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017080881. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29097622 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protein Mass Spectrometry Made Simple.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Jun;29(6):1585-1587. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018030244. Epub 2018 May 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29724882 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alpers CE, Kowalewska J: Fibrillary glomerulonephritis and immunotactoid glomerulopathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19: 34–37, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Alpers CE, Rennke HG, Hopper J Jr., Biava CG: Fibrillary glomerulonephritis: An entity with unusual immunofluorescence features. Kidney Int 31: 781–789, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary A, Gyamlani G, Cossey NL, Walker PD, Wall BM: Successful use of rituximab in fibrillary glomerulopathy. Ren Fail 36: 1151–1154, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Hogan J, Restivo M, Canetta PA, Herlitz LC, Radhakrishnan J, Appel GB, Bomback AS: Rituximab treatment for fibrillary glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29: 1925–1931, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Javaugue V, Karras A, Glowacki F, McGregor B, Lacombe C, Goujon JM, Ragot S, Aucouturier P, Touchard G, Bridoux F: Long-term kidney disease outcomes in fibrillary glomerulonephritis: A case series of 27 patients. Am J Kidney Dis 62: 679–690, 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

