Low dose nitrite improves reoxygenation following renal ischemia in rats
- PMID: 29097777
- PMCID: PMC5668317
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15058-5
Low dose nitrite improves reoxygenation following renal ischemia in rats
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Low dose nitrite improves reoxygenation following renal ischemia in rats.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 24;8(1):1748. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19651-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29367591 Free PMC article.
Abstract
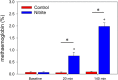
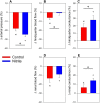
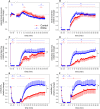
In hypoxic and acidic tissue environments, nitrite is metabolised to nitric oxide, thus, bringing about novel therapeutic options in myocardial infarction, peripheral artery disease, stroke, and hypertension. Following renal ischemia, reperfusion of the kidney remains incomplete and tissue oxygenation is reduced for several minutes to hours. Thus, in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, providing nitrite may have outstanding therapeutic value. Here we demonstrate nitrite's distinct potential to rapidly restore tissue oxygenation in the renal cortex and medulla after 45 minutes of complete unilateral kidney ischemia in the rat. Notably, tissue oxygenation was completely restored, while tissue perfusion did not fully reach pre-ischemia levels within 60 minutes of reperfusion. Nitrite was infused intravenously in a dose, which can be translated to the human. Specifically, methaemoglobin did not exceed 3%, which is biologically negligible. Hypotension was not observed. Providing nitrite well before ischemia and maintaining nitrite infusion throughout the reperfusion period prevented the increase in serum creatinine by ischemia reperfusion injury. In conclusion, low-dose nitrite restores renal tissue oxygenation in renal ischemia reperfusion injury and enhances regional kidney post-ischemic perfusion. As nitrite provides nitric oxide predominantly in hypoxic tissues, it may prove a specific measure to reduce renal ischemia reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

