Insight into the Mechanism of Action of Marine Cytotoxic Thiazinoquinones
- PMID: 29099042
- PMCID: PMC5706025
- DOI: 10.3390/md15110335
Insight into the Mechanism of Action of Marine Cytotoxic Thiazinoquinones
Abstract
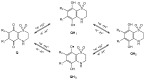
The electrochemical response of four natural cytotoxic thiazinoquinones isolated from the Aplidium species was studied using conventional solution-phase and solid-state techniques, based on the voltammetry of immobilized particles methodology. The interaction with O₂ and electrochemically generated reactive oxygen species (ROS) was electrochemically monitored. At the same time, a molecular modeling study including density functional theory (DFT) calculations was performed in order to analyze the conformational and electronic properties of the natural thiazinoquinones, as well as those of their reduced intermediates. The obtained electrochemical and computational results were analyzed and correlated to cytotoxic activity of these compounds, highlighting some features possibly related to their mechanism of action.
Keywords: DFT calculations; bioactive natural products; cytotoxic activity; electrochemistry; reactive radical species; thiazinoquinones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Zuman P., Perrin C.L. Organic Polarography. John Wiley & Sons; New York, NY, USA: 1969. pp. 1–316.
-
- Doménech-Carbó A., de Carvalho L.M., Martini M., Valencia D.P., Cebrián-Torrejón G. Electrochemical monitoring of the pharmacological activity of natural products. Stud. Nat. Prod. 2015;45:59–84. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63473-3.00003-4. - DOI
-
- De Campos Rodrigues T., Rosenbaum M.A. Microbial electroreduction: Screening for new cathodic biocatalysts. ChemElectroChem. 2014;1:1916–1922. doi: 10.1002/celc.201402239. - DOI
-
- TerAvest M.A., Zajdel T.J., Ajo-Franklin C.M. The Mtr pathway of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 couples substrate utilization to current production in Escherichia coli. ChemElectroChem. 2014;1:1874–1879. doi: 10.1002/celc.201402194. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

