Ammonia Reduces Intracellular Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Cultured Astrocytes Stimulating Its y⁺LAT2 Carrier-Mediated Loss
- PMID: 29099056
- PMCID: PMC5713277
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18112308
Ammonia Reduces Intracellular Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Cultured Astrocytes Stimulating Its y⁺LAT2 Carrier-Mediated Loss
Abstract
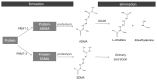
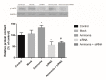
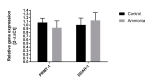
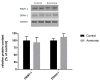
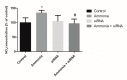
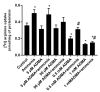
Previously we had shown that ammonia stimulates nitric oxide (NO) synthesis in astrocytes by increasing the uptake of the precursor amino acid, arginine via the heteromeric arginine/glutamine transporter y⁺LAT2. Ammonia also increases the concentration in the brain of the endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), but distribution of ADMA surplus between the intraastrocytic and extracellular compartments of the brain has not been studied. Here we tested the hypothesis that ammonia modulates the distribution of ADMA and its analog symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) between the two compartments of the brain by competition with arginine for the y⁺LAT2 transporter. In extension of the hypothesis we analyzed the ADMA/Arg interaction in endothelial cells forming the blood-brain barrier. We measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS) technique the concentration of arginine, ADMA and SDMA in cultured cortical astrocytes and in a rat brain endothelial cell line (RBE-4) treated with ammonia and the effect of silencing the expression of a gene coding y⁺LAT2. We also tested the expression of ADMA metabolism enzymes: protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) and dimethylarginine dimethyl aminohydrolase (DDAH) and arginine uptake to astrocytes. Treatment for 48 h with 5 mM ammonia led to an almost 50% reduction of ADMA and SDMA concentration in both cell types, and the effect in astrocytes was substantially attenuated by silencing of the Slc7a6 gene. Moreover, the y⁺LAT2-dependent component of ammonia-evoked arginine uptake in astrocytes was reduced in the presence of ADMA in the medium. Our results suggest that increased ADMA efflux mediated by upregulated y⁺LAT2 may be a mechanism by which ammonia interferes with intra-astrocytic (and possibly intra-endothelial cell) ADMA content and subsequently, NO synthesis in both cell types.
Keywords: ammonia; astrocytes; asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA); nitric oxide; rat brain endothelial cell line (RBE-4) cells; symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA); y+LAT2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in ammonia-exposed cultured astrocytes is coupled to increased arginine transport by upregulated y(+)LAT2 transporter.J Neurochem. 2015 Dec;135(6):1272-81. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13387. Epub 2015 Nov 6. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26448619
-
Increased symmetrical dimethylarginine in ischemic acute kidney injury as a causative factor of renal L-arginine deficiency.Transl Res. 2013 Aug;162(2):67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 May 22. Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23707198
-
Upregulation of the heteromeric y⁺LAT2 transporter contributes to ammonia-induced increase of arginine uptake in rat cerebral cortical astrocytes.Neurochem Int. 2012 Sep;61(4):531-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.02.021. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Neurochem Int. 2012. PMID: 22401943
-
Toxic Dimethylarginines: Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) and Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA).Toxins (Basel). 2017 Mar 6;9(3):92. doi: 10.3390/toxins9030092. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28272322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA): a promising biomarker for cardiovascular disease?Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(2):180-200. doi: 10.2174/1568026611313020007. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23470077 Review.
Cited by
-
Disturbances in Nitric Oxide Cycle and Related Molecular Pathways in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;15(24):5797. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245797. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asymmetric dimethylarginine induces maladaptive function of the blood-brain barrier.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 9;12:1476386. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1476386. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39445335 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor cell-derived asymmetric dimethylarginine regulates macrophage functions and polarization.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Nov 15;22(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02769-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36376929 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Astrocytic Glutamine Transport in Acute Hyperammonemic Brain Edema.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 6;16:874750. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.874750. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35733937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transport of L-Arginine Related Cardiovascular Risk Markers.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 8;9(12):3975. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123975. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33302555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nauser T., Koppenol W.H. The rate constant of the reaction of superoxide with nitrogen monoxide: Approaching the diffusion limit. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2002;106:4084–4086. doi: 10.1021/jp025518z. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

