A nation-wide multicenter 10-year (1999-2008) retrospective study of chemotherapy in Chinese breast cancer patients
- PMID: 29100275
- PMCID: PMC5652669
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16439
A nation-wide multicenter 10-year (1999-2008) retrospective study of chemotherapy in Chinese breast cancer patients
Abstract
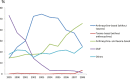
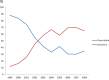
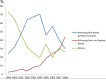
Little information is available on the evolvement of chemotherapeutic regimens administered to Chinese females with breast cancer. We retrospectively analyzed demographic, pathological and chemotherapeutic data of 4211 breast cancer patients, who were randomly selected from representative hospitals of 7 traditional areas in China between 1999 and 2008. A total of 3271 cases (77.7%) received adjuvant chemotherapy, 558 (13.3%) received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and 392 (9.3%) received chemotherapy for metastatic disease. In the adjuvant setting, higher percentage of patients with younger age, advanced stage, hormone receptor (HR) negative or HER2 positive disease received chemotherapy (P<0.001). The use of CMF (cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil) in adjuvant chemotherapy decreased significantly from 1999 to 2008, while the use of anthracycline-based (without taxanes) regimens increased in the first 5 years, followed by increased use of regimens containing both anthracyclines and taxanes. Women with locally advanced disease received more neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The percentage of neoadjuvant regimens containing anthracyclines and taxanes increased during this period. In first-line chemotherapy of metastatic disease, 87.5% of cases received combined chemotherapy, and platinum-based regimens were also major choices aside from anthracyclines and taxanes. In second-line chemotherapy, 80.3% received combined chemotherapy, and the combination of taxane and platinum was the most common choice. In conclusion, major changes have taken place in breast cancer chemotherapy in China during this 10-year interval, which reflected the incorporation of key evidence and guidelines into Chinese medical practice.
Keywords: PDAC; SREBP; diabetes; insulin; transgelin2.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Major changes in chemotherapy regimens administered to breast cancer patients during 2000-2008 in the Netherlands.Breast J. 2013 Jul-Aug;19(4):394-401. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12125. Epub 2013 May 12. Breast J. 2013. PMID: 23663128
-
Sequencing of anthracyclines and taxanes in neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for early breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 18;2(2):CD012873. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012873.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30776132 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Analysis of Metronomic Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate, and Fluorouracil (CMF) Versus Docetaxel and Cyclophosphamide (TC) as Adjuvant Treatment in Early Stage, Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Negative Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2022 Apr;22(3):e310-e318. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2021.09.007. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Clin Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34753632
-
Taxanes for adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 2;9(9):CD004421. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004421.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31476253 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer.Dan Med J. 2016 May;63(5):B5222. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27127018 Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of postoperative adjuvant therapy for small bowel adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 10;13(8):e0200204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200204. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30096150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profile, treatment patterns, and influencing factors of anthracycline use in breast cancer patients in China: A nation-wide multicenter study.Cancer Med. 2021 Oct;10(19):6744-6761. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4215. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34472719 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment patterns for adjuvant docetaxel-based chemotherapy in early-stage breast cancer in China: A pooled retrospective analysis of four observational studies.Chin J Cancer Res. 2018 Jun;30(3):327-339. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.03.05. Chin J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30046227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Moliterni A, Zambetti M, Brambilla C. Adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil in node-positive breast cancer: the results of 20 years of follow-up. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:901–6. - PubMed
-
- Ring AE, Ellis PA. Taxanes in the treatment of early breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2005;31:618–27. - PubMed
-
- Henderson IC, Berry DA, Demetri GD, Cirrincione CT, Goldstein LJ, Martino S, Ingle JN, Cooper MR, Hayes DF, Tkaczuk KH, Fleming G, Holland JF, Duggan DB. Improved outcomes from adding sequential Paclitaxel but not from escalating Doxorubicin dose in an adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for patients with node-positive primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:976–83. - PubMed
-
- Tkaczuk KH. Review of the contemporary cytotoxic and biologic combinations available for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Clin Ther. 2009;31(Pt 2):2273–89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

