Effect of TALEN-mediated IL-6 knockout on cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and anti-cancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC-LM3) cells
- PMID: 29100435
- PMCID: PMC5652824
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20946
Effect of TALEN-mediated IL-6 knockout on cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and anti-cancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC-LM3) cells
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the exact effect of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and anti-cancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Experimental design: IL-6 was disrupted by transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN) in HCCLM3 cells, and was used to evaluate the role of IL-6 on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and key signaling pathways involved in sorafenib and/or IFNα therapy.
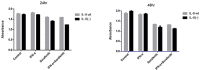
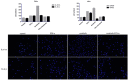
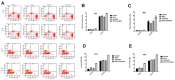
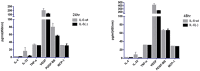
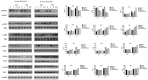
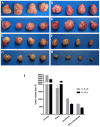
Results: IL-6 has no direct effect on cell proliferation and invasion but promotes cell apoptosis and up-regulate IL-33 and VEGF-A expression. IL-6 could attenuate the anti-proliferation effect by sorafenib and combination therapy but facilitate the pro-apoptosis of the combination therapy and augment the pro-invasive effect induced by single treatment. IL-6 could down-regulate p-STAT3, however up-regulate the p-MEK/p-ERK and NF-kB/iNOS expression, and it also facilitated the promotion on p-JAK2 and p-MEK/p-ERK by either sorafenib or IFN-α. in vivo study, IL-6 significantly promotes tumor growth. The combination treatment showed the highest inhibition on tumor growth which is derived from HCCLM3-IL6(-) cells.
Conclusions: IL-6 has no direct effect on cell proliferation and invasion but promotes tumor cell apoptosis in vitro study. Sorafenib and combination therapies are suitable for HCC cells with low or no IL-6 expression confirmed in vivo study.
Keywords: IL-6; TALEN; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
YC-1 enhances the anti-tumor activity of sorafenib through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2014 Jan 13;13:7. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-7. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24418169 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-α enhances antitumor activities of oncolytic adenovirus-mediated IL-24 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2012 May 8;11:31. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-31. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22569271 Free PMC article.
-
The HDAC Inhibitor Quisinostat (JNJ-26481585) Supresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma alone and Synergistically in Combination with Sorafenib by G0/G1 phase arrest and Apoptosis induction.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Oct 20;14(13):1845-1858. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.27661. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30443188 Free PMC article.
-
Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5.Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 15;66(24):11851-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1377. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17178882
-
A novel multitarget kinase inhibitor BZG with potent anticancer activity in vitro and vivo enhances efficacy of sorafenib through PI3K pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 May;125:110033. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110033. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32187962
Cited by
-
Downregulation of hypermethylated in cancer-1 by miR-4532 promotes adriamycin resistance in breast cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Sep 4;18:127. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0616-x. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30202238 Free PMC article.
-
IL‑6 plays a crucial role in epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and pro‑metastasis induced by sorafenib in liver cancer.Oncol Rep. 2021 Mar;45(3):1105-1117. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7926. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33432366 Free PMC article.
-
Genome editing via non-viral delivery platforms: current progress in personalized cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 11;21(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01550-8. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35277177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum IL-6 predicts immunotherapy-related adverse and outcome in advanced gastric and esophageal cancer patients with Anti-PD-1 treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 May 30;16:1553882. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1553882. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40519900 Free PMC article.
-
CircFMN2 Boosts Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Upregulating CNBP by Restraining Ubiquitination.J Oncol. 2022 Jul 21;2022:2674163. doi: 10.1155/2022/2674163. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35909906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang S, Yuan Y, He Y, Pan D, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Liu Q, Zhang Z, Liu Z. Genetic polymorphism of interleukin-6 influences susceptibility to HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in a male Chinese Han population. Hum Immunol. 2014;75:297–301. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

