Effect of TALEN-mediated IL-6 knockout on cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and anti-cancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC-LM3) cells
- PMID: 29100435
- PMCID: PMC5652824
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20946
Effect of TALEN-mediated IL-6 knockout on cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and anti-cancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC-LM3) cells
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the exact effect of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and anti-cancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Experimental design: IL-6 was disrupted by transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN) in HCCLM3 cells, and was used to evaluate the role of IL-6 on tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and key signaling pathways involved in sorafenib and/or IFNα therapy.
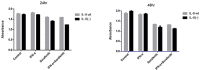
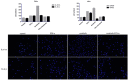
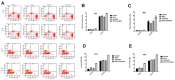
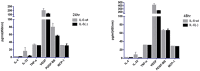
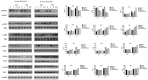
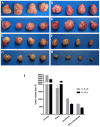
Results: IL-6 has no direct effect on cell proliferation and invasion but promotes cell apoptosis and up-regulate IL-33 and VEGF-A expression. IL-6 could attenuate the anti-proliferation effect by sorafenib and combination therapy but facilitate the pro-apoptosis of the combination therapy and augment the pro-invasive effect induced by single treatment. IL-6 could down-regulate p-STAT3, however up-regulate the p-MEK/p-ERK and NF-kB/iNOS expression, and it also facilitated the promotion on p-JAK2 and p-MEK/p-ERK by either sorafenib or IFN-α. in vivo study, IL-6 significantly promotes tumor growth. The combination treatment showed the highest inhibition on tumor growth which is derived from HCCLM3-IL6(-) cells.
Conclusions: IL-6 has no direct effect on cell proliferation and invasion but promotes tumor cell apoptosis in vitro study. Sorafenib and combination therapies are suitable for HCC cells with low or no IL-6 expression confirmed in vivo study.
Keywords: IL-6; TALEN; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tang S, Yuan Y, He Y, Pan D, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Liu Q, Zhang Z, Liu Z. Genetic polymorphism of interleukin-6 influences susceptibility to HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in a male Chinese Han population. Hum Immunol. 2014;75:297–301. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

