Carrot intake and incidence of urothelial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29100438
- PMCID: PMC5652827
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19832
Carrot intake and incidence of urothelial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
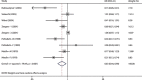
Previous studies regarding the relationship between carrot intake and risk of urothelial cancer have reported conflicting results. Hence we performed a meta-analysis of eligible studies to summarize evidence on this association. A comprehensive search up to January 2017 was performed in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, EMBASE, Cochrane register, and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases. The combined odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) for the highest versus the lowest intake of carrot was calculated. A total of six epidemiological studies consisting of four case-control and two cohort studies were included. Overall analysis indicated a significantly reduced risk of urothelial cancer for high intake of carrot (OR = 0.63, 95% CI 0.44-0.90). Obvious significant heterogeneity was observed among included studies (P < 0.001 for heterogeneity; I2 = 79.6%). There was no significant publication bias by Begg's test (P = 0.348) or Egger's test (P = 0.130). In conclusion, this meta-analysis indicates that high intake of carrot is associated with a low incidence of urothelial cancer. Considering the limited included studies and huge heterogeneity, further large well-designed prospective cohort studies are warranted to confirm the findings from our meta-analysis.
Keywords: carrot; meta-analysis; risk; urothelial cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dietary carrot consumption and the risk of prostate cancer.Eur J Nutr. 2014 Dec;53(8):1615-23. doi: 10.1007/s00394-014-0667-2. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Eur J Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24519559 Review.
-
Cruciferous vegetable consumption and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2015 Feb 12;13:44. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0454-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25889229 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection and pancreatic cancer risk: A meta-analysis.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C229-C232. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200744. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230023
-
No association between fiber intake and prostate cancer risk: a meta-analysis of epidemiological studies.World J Surg Oncol. 2015 Aug 28;13:264. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0681-8. World J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26315558 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Cadmium Exposure and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 10;9:555539. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.555539. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35223753 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of Dietary Carrot Intake With Bladder Cancer Risk in a Prospective Cohort of 99,650 Individuals With 12.5 Years of Follow-Up.Front Nutr. 2021 Jul 26;8:669630. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.669630. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34381804 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A and Retinoids in Bladder Cancer Chemoprevention and Treatment: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence, Challenges and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 29;22(7):3510. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073510. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Dietary Carrot/Carotene Intakes With Colorectal Cancer Incidence and Mortality in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial.Front Nutr. 2022 Jun 17;9:888898. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.888898. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35782935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat SF, van Rhijn BW, Comperat E, Sylvester RJ, Kaasinen E, Bohle A, Palou Redorta J, Roupret M. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol. 2013;64:639–653. - PubMed
-
- Colin P, Koenig P, Ouzzane A, Berthon N, Villers A, Biserte J, Roupret M. Environmental factors involved in carcinogenesis of urothelial cell carcinomas of the upper urinary tract. BJU Int. 2009;104:1436–1440. - PubMed
-
- Shinka T, Miyai M, Sawada Y, Inagaki T, Okawa T. Factors affecting the occurrence of urothelial tumors in dye workers exposed to aromatic amines. Int J Urol. 1995;2:243–248. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

