Correction to: Gene-environment interaction between lead and Apolipoprotein E4 causes cognitive behavior deficits in mice
- PMID: 29100536
- PMCID: PMC5670524
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-017-0223-7
Correction to: Gene-environment interaction between lead and Apolipoprotein E4 causes cognitive behavior deficits in mice
Figures
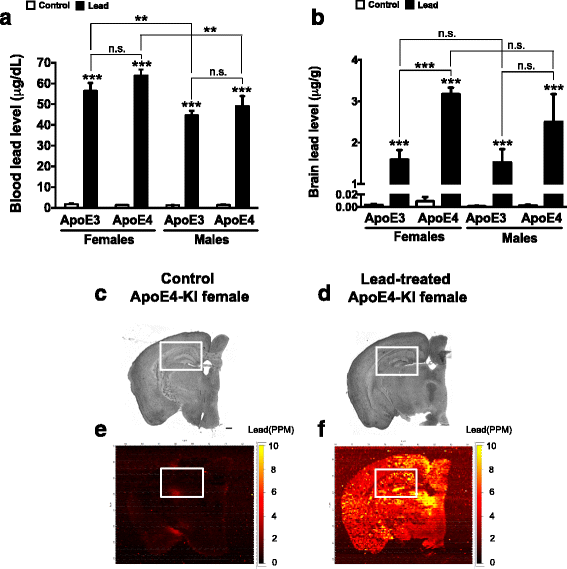
Erratum for
-
Gene-environment interaction between lead and Apolipoprotein E4 causes cognitive behavior deficits in mice.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Feb 7;12(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0155-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28173832 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Gene-environment interaction between lead and Apolipoprotein E4 causes cognitive behavior deficits in mice.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Feb 7;12(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0155-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28173832 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 genotype compromises brain exosome production.Brain. 2019 Jan 1;142(1):163-175. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy289. Brain. 2019. PMID: 30496349 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid prevents cognitive deficits in human apolipoprotein E epsilon 4-targeted replacement mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Sep;57:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 May 10. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28595105
-
Apolipoprotein E4 and Insulin Resistance Interact to Impair Cognition and Alter the Epigenome and Metabolome.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 8;7:43701. doi: 10.1038/srep43701. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28272510 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol drinking in middle age and subsequent risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia in old age: a prospective population based study.BMJ. 2004 Sep 4;329(7465):539. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38181.418958.BE. Epub 2004 Aug 10. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15304383 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cadmium, an Environmental Contaminant, Exacerbates Alzheimer's Pathology in the Aged Mice's Brain.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jun 24;13:650930. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.650930. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34248598 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

