T cells upon activation promote endothelin 1 production in monocytes via IFN-γ and TNF-α
- PMID: 29101349
- PMCID: PMC5670167
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14202-5
T cells upon activation promote endothelin 1 production in monocytes via IFN-γ and TNF-α
Abstract
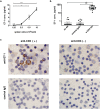
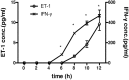
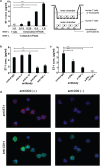
Endothelin 1 (ET-1), mainly produced from vascular endothelial cells, induces vasoconstriction in physiological conditions. The endothelin receptor antagonist is among the most effective agents for pulmonary hypertension. However, little is known about the production source of ET-1 in inflammation and immunity. Here, we studied whether T cell-mediated ET-1 production system exists and operates independent of the production system in vascular endothelial cells. ET-1 production was readily detectable in the culture supernatant of human PBMCs and murine spleen cells stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody. Immunocytostaining showed that ET-1-producing cells emerged only in PBMCs stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody. Using the Transwell system, both murine and human monocytes sorted with magnetic beads in the inner chamber produced ET-1 when T cells were activated with antigen or anti-CD3 antibody in the outer chamber. This ET-1 production was inhibited by anti-IFN-γ and/or TNF-α antibody. Furthermore, monocytes purified from ETflox/flox;Tie2-Cre( + ) mice, which conditionally lack ET-1 in hematopoietic stem cells and vascular endothelial cells, did not produce ET-1 even when stimulated by antigen-specific T cell activation. This study demonstrates the existence of an immune-mediated ET-1 production induced by T cells upon activation through IFN-γ and TNF-α.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

