FT-IR Spectroscopy Study in Early Diagnosis of Skin Cancer
- PMID: 29102935
- PMCID: PMC5756641
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11179
FT-IR Spectroscopy Study in Early Diagnosis of Skin Cancer
Abstract
Background/aim: Mid-infrared spectroscopy (4000-500 cm-1) was used to analyze the spectral changes and differences of the characteristic absorption bands of the skin components due to cancer development for early clinical diagnosis.
Materials and methods: Human biopsies from basal cell carcinoma, malignant melanoma, and nevus were used, while normal skin tissue served as a control.
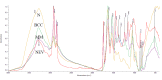
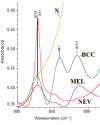
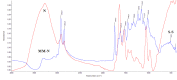
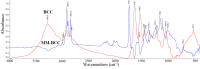
Results: The high quality of Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra showed that upon cancer development the intensity of the absorption band at approximately 3062 cm-1 was increased, indicating that most of the proteins had the configuration of amide B and the β-sheet protein structure predominated. The stretching vibration bands of vCH2 in the region 2950-2850 cm-1 were increased in melanoma and nevus, while were less pronounced in basal cell carcinoma due to the increased lipophilic environment. In addition, the intensity of a new band at 1744 cm-1, which is assigned to aldehyde, was increased in melanoma and nevus and appeared as a shoulder in the spectra of normal skin. The absorption band of amide I at 1650 cm-1 was split into two bands, at 1650 cm-1 and 1633 cm-1, due to the presence of both α-helix and random coil protein conformations for melanoma and nevus. This was confirmed from the amide II band at 1550 cm-1, which shifted to lower frequencies at 1536 cm-1 and 1540 cm-1 for basal cell carcinoma and melanoma, respectively, indicating a damage of the native structure of proteins. The bands at 841 and 815 cm-1, which are assigned to B-DNA and Z-DNA, respectively, indicated that only the bands of the cancerous Z-DNA form are pronounced in melanoma, while in BCC both the characteristic bands of B-DNA and Z-DNA forms are found.
Conclusion: It is proposed that the bands described above could be used as "diagnostic marker" bands for DNA forms, in the diagnosis of skin cancer.
Keywords: Skin cancer; basal cell carcinoma (BCC); diagnostic bands; infrared spectroscopy; melanoma (MM); nevous (NEV).
Copyright© 2017, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Seebode C, Lehmann J, Emmert S. Photocarcinogenesis and skin cancer prevention strategies. Anticancer Res. 2016;33(3):1371–1378. - PubMed
-
- Grammenandi K, Kyriazi M, Katsarou-Katsari A, Papadopoulos O, Anastassopoulou I, Papaioannou GT, Sagriotis A, Rallis M, Maibach HI. Low-molecular-weight hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants in nonmelanoma skin carcinomas and adjacent normal-looking skin. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;29:324–333. - PubMed
-
- Delinasios G. UVA-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in human skin cells and photoprotection by antioxidant compounds. PhD Thesis, King’s College, London, UK. 2012
-
- Brauche E, Johannsen H, Nolag S, Trude S, Schenke-Layland Design and analysis of a squamous cell carcinoma in vitro model system. Biomaterials. 2014;34:7401–7407. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
