Fibrotic Lung Toxicity Induced by Hydroxycarbamide
- PMID: 29102950
- PMCID: PMC5756656
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11194
Fibrotic Lung Toxicity Induced by Hydroxycarbamide
Abstract
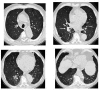
A patient treated for 4 months with hydroxycarbamide (hydroxyurea) for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia was admitted to hospital for recently developed severe dyspnea and acute respiratory failure. The computed tomographic scan of the chest showed diffuse ground glass opacities, some centrilobular low-density nodules (resembling hypersensitivity pneumonitis-like pattern), and minimal interstitial reticulation of the subpleural region. The analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid excluded infection, as did serological examinations. The patient was started on oxygen therapy and with relief of thrombocytopenia and suspected hemolytic anemia, hydroxyurea treatment was discontinued. The patient underwent steroid therapy, with a rapid progressive improvement of clinical and radiological features. As hydroxyurea is increasingly used for a number of systemic disorders, physicians must be aware of its potential lung toxicity, requiring immediate cessation of the treatment and empiric corticosteroid therapy.
Keywords: Hydroxycarbamide; case report; hydroxyurea; interstitial pneumonitis; lung toxicity.
Copyright© 2017, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Finazzi G, Ruggeri M, Rodeghiero F, Barbui T. Hydroxyurea for patients with essential thrombocythemia and a high risk of thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1132–1136. - PubMed
-
- Grandi V, Delfino C, Pimpinelli N. Ingenol mebutate in the treatment of ‘hydroxyurea-induced squamous dysplasia’: a single-centre experience. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30(7):1129–1132. - PubMed
-
- Blanc PL, Joasson JM, Hammoud H, Matussière Y. Acute interstitial pneumopathy with fever caused by hydroxyurea. Presse Med. 2000;29(5):242–245. - PubMed
-
- Internullo M, Giannelli V, Sardo L, Antonaglia C, Villani T, Angelici E, Palange P. Hydroxyurea-induced interstitial pneumonitis: case report and review of the literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(2):190–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials