Examining the Relationship between Trace Lithium in Drinking Water and the Rising Rates of Age-Adjusted Alzheimer's Disease Mortality in Texas
- PMID: 29103043
- PMCID: PMC7592673
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-170744
Examining the Relationship between Trace Lithium in Drinking Water and the Rising Rates of Age-Adjusted Alzheimer's Disease Mortality in Texas
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) mortality rates have steadily increased over time. Lithium, the current gold standard treatment for bipolar disorder, can exert neuroprotective effects against AD.
Objective: We examined the relationship between trace levels of lithium in drinking water and changes in AD mortality across several Texas counties.
Methods: 6,180 water samples from public wells since 2007 were obtained and averaged for 234 of 254 Texas counties. Changes in AD mortality rates were calculated by subtracting aggregated age-adjusted mortality rates obtained between 2000-2006 from those obtained between 2009-2015. Using aggregated rates maximized the number of counties with reliable mortality data. Correlational analyses between average lithium concentrations and changes in AD mortality were performed while also adjusting for gender, race, education, rural living, air pollution, physical inactivity, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
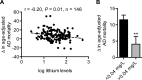
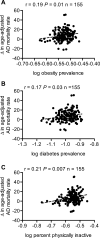
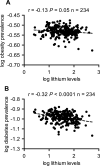
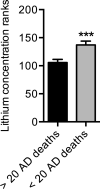
Results: Age-adjusted AD mortality rate was significantly increased over time (+27%, p < 0.001). Changes in AD mortality were negatively correlated with trace lithium levels (p = 0.01, r = -0.20), and statistical significance was maintained after controlling for most risk factors except for physical inactivity, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes positively correlated with changes in AD mortality (p = 0.01 and 0.03, respectively), but also negatively correlated with trace lithium in drinking water (p = 0.05 and <0.0001, respectively).
Conclusion: Trace lithium in water is negatively linked with changes in AD mortality, as well as obesity and type 2 diabetes, which are important risk factors for AD.
Keywords: Dementia; GSK3; neuroprotection; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased Prevalence of Obesity/Type 2 Diabetes and Lower Levels of Lithium in Rural Texas Counties May Explain Greater Alzheimer's Disease Risk.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;64(1):303-308. doi: 10.3233/JAD-171150. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29865052
-
Trace lithium in Texas tap water is negatively associated with all-cause mortality and premature death.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018 Apr;43(4):412-414. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2017-0653. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018. PMID: 29206474
-
Lithium in the public water supply and suicide mortality in Texas.J Psychiatr Res. 2013 Mar;47(3):407-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Psychiatr Res. 2013. PMID: 23312137
-
Association between naturally occurring lithium in drinking water and suicide rates: systematic review and meta-analysis of ecological studies.Br J Psychiatry. 2020 Dec;217(6):667-678. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2020.128. Br J Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32716281
-
Using Multicountry Ecological and Observational Studies to Determine Dietary Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease.J Am Coll Nutr. 2016 Jul;35(5):476-89. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2016.1161566. J Am Coll Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27454859 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress and trends of research on mineral elements for depression.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 31;10(15):e35469. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35469. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170573 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effect of the novel ionic cocrystal of lithium salicylate proline (LISPRO) with lithium carbonate and lithium salicylate on memory and behavior in female APPswe/PS1dE9 Alzheimer's mice.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Sep;97(9):1066-1080. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24438. Epub 2019 May 17. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 31102295 Free PMC article.
-
Bipolar disorder and Lewy body dementia: case report and literature review.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 4;15:1409027. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1409027. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38895028 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium: how low can you go?Int J Bipolar Disord. 2024 Jan 30;12(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40345-024-00325-y. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2024. PMID: 38289425 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lithium and its effects: does dose matter?Int J Bipolar Disord. 2024 Jun 24;12(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40345-024-00345-8. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2024. PMID: 38914810 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

