Polygenic risk score in postmortem diagnosed sporadic early-onset Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29103623
- PMCID: PMC5995122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.09.035
Polygenic risk score in postmortem diagnosed sporadic early-onset Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
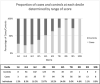
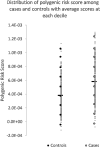
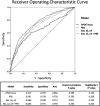
Sporadic early-onset Alzheimer's disease (sEOAD) exhibits the symptoms of late-onset Alzheimer's disease but lacks the familial aspect of the early-onset familial form. The genetics of Alzheimer's disease (AD) identifies APOEε4 to be the greatest risk factor; however, it is a complex disease involving both environmental risk factors and multiple genetic loci. Polygenic risk scores (PRSs) accumulate the total risk of a phenotype in an individual based on variants present in their genome. We determined whether sEOAD cases had a higher PRS compared to controls. A cohort of sEOAD cases was genotyped on the NeuroX array, and PRSs were generated using PRSice. The target data set consisted of 408 sEOAD cases and 436 controls. The base data set was collated by the International Genomics of Alzheimer's Project consortium, with association data from 17,008 late-onset Alzheimer's disease cases and 37,154 controls, which can be used for identifying sEOAD cases due to having shared phenotype. PRSs were generated using all common single nucleotide polymorphisms between the base and target data set, PRS were also generated using only single nucleotide polymorphisms within a 500 kb region surrounding the APOE gene. Sex and number of APOE ε2 or ε4 alleles were used as variables for logistic regression and combined with PRS. The results show that PRS is higher on average in sEOAD cases than controls, although there is still overlap among the whole cohort. Predictive ability of identifying cases and controls using PRSice was calculated with 72.9% accuracy, greater than the APOE locus alone (65.2%). Predictive ability was further improved with logistic regression, identifying cases and controls with 75.5% accuracy.
Keywords: Genotyping; NeuroChip; NeuroX; Polygenic risk score (PRS); Sporadic early-onset Alzheimer's disease (sEOAD).
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polygenic risk score of sporadic late-onset Alzheimer's disease reveals a shared architecture with the familial and early-onset forms.Alzheimers Dement. 2018 Feb;14(2):205-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.08.013. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2018. PMID: 28943286 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic risk and hazard scores for Alzheimer's disease prediction.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019 Feb 18;6(3):456-465. doi: 10.1002/acn3.716. eCollection 2019 Mar. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30911569 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic risk of Alzheimer's disease in the Faroe Islands.Eur J Neurol. 2022 Aug;29(8):2192-2200. doi: 10.1111/ene.15351. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Eur J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35384166
-
From Polygenic Scores to Precision Medicine in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;74(4):1271-1283. doi: 10.3233/JAD-191233. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32250305 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the association between the APOE gene and the risk of Alzheimer's disease: possible roles for APOE promoter polymorphisms and alterations in APOE transcription.J Neurochem. 2003 Mar;84(6):1215-36. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01615.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12614323 Review.
Cited by
-
Unique Pathology in the Locus Coeruleus of Individuals with Down Syndrome.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;101(2):541-561. doi: 10.3233/JAD-240043. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 39213062 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic landscape of early-onset Alzheimer's disease in China.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Feb;21(2):e14486. doi: 10.1002/alz.14486. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 39907198 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Patients With Degenerative Dementia Through the Whole Exome Sequencing.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Oct 14;13:745407. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.745407. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34720994 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic risk of Alzheimer's disease beyond APOE ε4: systematic review of Alzheimer's genetic risk scores.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Aug 24;8(1):166. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0221-8. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30143603 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic Risk Scores in Myocardial Injury After Noncardiac Surgery: A VISION Substudy.JACC Adv. 2025 Apr;4(4):101680. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.101680. Epub 2025 Mar 26. JACC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40147046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams HH, de Bruijn RF, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, van Duijn CM, Vernooij MW, Koudstaal PJ, Ikram MA. Genetic risk of neurodegenerative diseases is associated with mild cognitive impairment and conversion to dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2015;11:1277–1285. - PubMed
-
- Barber I, Braae A, Clement N, Patel T, Guetta-Baranes T, Brookes K, Medway C, Chappell S, Guerreiro R, Bras J, Hernandez D, Singleton A, Hardy J, Mann D, ARUK Consortium. Morgan K. Mutational analysis of sporadic early-onset Alzheimer’s disease using the NeuroX array. Neurobiol. Aging. 2017;49:215.e1–215.e8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blauwendraat C, Faghri F, Pihlstrom L, Geiger JT, Elbaz A, Lesage S, Corvol J, May P, Ryten M, Ferrari R, Bras J, Guerreiro R, Williams J, Sims R, Lubbe S, Hernandez DG, Mok KY, Robak L, Campbell RH, Rogaeva E, Traynor BJ, Chia R, Chung SJ, International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC) COURAGE-PD Consortium. Hardy JA, Brice A, Wood NW, Houlden H, Shulman JM, Morris HR, Gasser T, Krüger R, Heutink P, Sharma M, Simón Sánchez J, Nalls MA, Singleton AB, Scholz SW. NeuroChip, an updated version of the NeuroX genotyping platform to rapidly screen for variants associated with neurological diseases. Neurobiol. Aging. 2017;57:247.e9–247.e13. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 200/ALZS_/Alzheimer's Society/United Kingdom
- G1100540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0502157/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0400074/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 082604/2/07/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0900652/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000950/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 503480/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

